[ad_1]
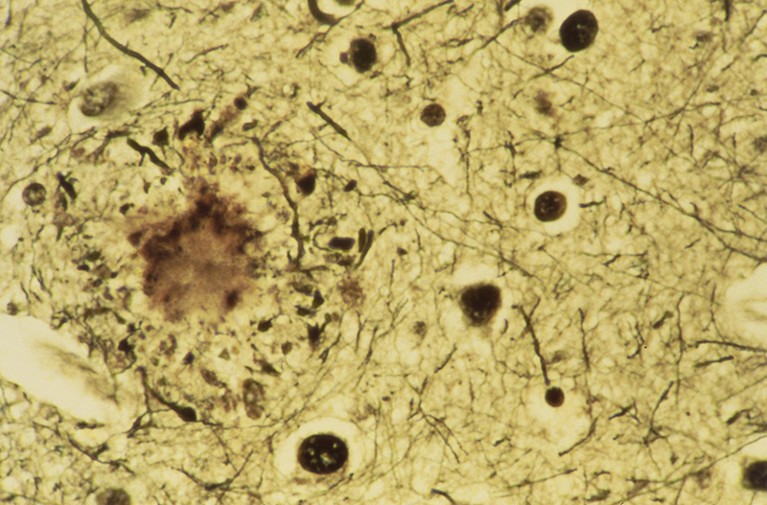
Folks with Alzheimer’s illness often develop protein plaques (round splotch on left) of their brains.Credit score: Science Picture Library
Some researchers are celebrating this week’s announcement {that a} drug candidate for Alzheimer’s illness slowed the speed of cognitive decline for individuals in a scientific trial by 27%. Others, nevertheless, stay hesitant, desirous to see knowledge past what was disclosed in a 27 September press launch. If the outcomes get up, the remedy — referred to as lecanemab — could be the primary of its form to point out a powerful sign of cognitive profit in a sturdy trial.
“It’s such a win for our subject,” says Liana Apostolova, a neurologist on the Indiana College Faculty of Drugs in Indianapolis.
Extra Alzheimer’s medication head for FDA evaluation: what scientists are watching
The outcomes are “fairly promising”, says Caleb Alexander, an internal-medicine specialist and epidemiologist on the Johns Hopkins Bloomberg Faculty of Public Well being in Baltimore, Maryland, and an advisory committee member for the US Meals and Drug Administration (FDA). However, he provides, “we’ll should see what the complete evaluation of the trial suggests”. Alexander and others additionally be aware that, though the outcomes point out that lecanemab does present some scientific profit, the diploma to which it does so is small.
Developed by Eisai, a pharmaceutical firm in Tokyo, and biotechnology agency Biogen in Cambridge, Massachusetts, lecanemab is a monoclonal antibody designed to clear clumps of protein from the mind that many assume are a root reason behind Alzheimer’s illness. This concept, referred to as the ‘amyloid speculation’, holds that the protein amyloid-β accumulates into poisonous deposits because the illness progresses, finally inflicting dementia.
Controversial Alzheimer’s drug approval might have an effect on different illnesses
Whether or not or not lecanemab confirms the amyloid speculation stays to be seen, researchers say.
“I don’t assume one examine will show a really long-standing controversial speculation,” says Brent Forester, director of the Geriatric Psychiatry Analysis Program at McLean Hospital in Belmont, Massachusetts, who helped to run the scientific trial for lecanemab. “However one optimistic examine helps the speculation.”
Amyloid is “related to the issue, nevertheless it isn’t ‘the’ drawback”, says George Perry, a neurobiologist on the College of Texas at San Antonio and a sceptic of the amyloid speculation. “In the event you modulate it, after all you possibly can have some small profit.”
Small, however vital
Even a modest profit would in all probability be appreciated by the tens of thousands and thousands of individuals residing with Alzheimer’s illness worldwide. “These are essentially the most encouraging leads to scientific trials treating the underlying causes of Alzheimer’s to this point,” stated the Alzheimer’s Affiliation, a analysis funder and affected person advocacy group, in an announcement.
Final yr, the FDA controversially accepted aducanumab, one other monoclonal antibody developed by Biogen, to deal with Alzheimer’s — with out a clear sign of cognitive profit. Two incomplete section III trials demonstrated that the drug might clear amyloid from the mind, however just one subset of individuals confirmed a slowing in cognitive decline.
Landmark Alzheimer’s drug approval confounds analysis group
In contrast, lecanemab’s section III trial, referred to as Readability AD, ran uninterrupted for a full 18 months and slowed decline to a statistically vital extent. The topline outcomes launched by Eisai and Biogen describe findings from nearly 1,800 individuals with early-stage Alzheimer’s illness residing in additional than a dozen international locations.
Members acquired intravenous infusions of both lecanemab or a placebo each two weeks during the trial. Their cognition was assessed utilizing an 18-point scale referred to as the Medical Dementia Ranking–Sum of Bins (CDR–SB). Clinicians calculate an individual’s CDR–SB rating by interviewing them and their carers, and testing the individual’s talents in areas equivalent to reminiscence and drawback fixing.
Not solely did lecanemab lower amyloid in individuals’s brains, however these receiving remedy scored, on common, 0.45 factors higher on the CDR-SB than these within the placebo group on the 18-month mark.
Will the FDA change the way it vets medication following the Alzheimer’s debacle?
It’s a “actually tiny and nearly unnoticeable distinction from placebo”, says Rob Howard, a psychiatrist at College School London. Though he and others differ in what a clinically vital end result could be, they provide a spread of 0.5 to 2 factors.
Nonetheless, lecanemab may very well be accepted as a drug on the premise of the info. The query might be whether or not the profit it brings is well worth the dangers. Through the trial, about 20% of individuals who acquired lecanemab confirmed abnormalities on their mind scans that indicated swelling or bleeding, though lower than 3% of these within the remedy group skilled signs of those uncomfortable side effects. In contrast, throughout the section III trials for aducanumab, 40% of individuals confirmed indicators of mind swelling on their scans.
Intently watched
The FDA is reviewing lecanemab for ‘accelerated approval’ on the premise of section II outcomes that confirmed a lower in amyloid. The brand new section III outcomes might tip the scales in favour of approval, though they aren’t formally a part of the evaluation. The company expects to announce its resolution on 6 January.
“It’s clear that everyone’s going to be watching this one carefully — as they need to be,” Alexander says. The FDA accepted aducanumab utilizing the identical programme, he says, so a precedent has been set that might have an effect on future anti-amyloid medication.
May medication stop Alzheimer’s? These trials purpose to seek out out
Biotech agency Roche, based mostly in Basel, Switzerland, will launch section III outcomes later this yr for its antibody, gantenerumab. And Eli Lilly, in Indianapolis, plans to publish outcomes for its candidate, donanemab, subsequent yr.
Researchers say that amyloid is just one element of Alzheimer’s illness, nevertheless.
“There’s a very detrimental second protein referred to as tau that must be addressed,” says Apostolova, who has consulted for Biogen and Eisai. Tau additionally deposits within the brains of people that have Alzheimer’s. “And tau is definitely the one that basically strongly correlates with cognitive decline,” she provides.
A multi-drug method concentrating on each amyloid and tau “could be essentially the most profitable by way of a relentless neurodegenerative illness equivalent to Alzheimer’s”, Apostolova says.
Forester widens that idea even additional, suggesting that folks with Alzheimer’s, and their carers, want assist past medicine, together with schooling and steering on methods to handle illness development.
“All of this needs to be part of holistic dementia care,” Forester says. “You’ll be able to’t intervene with a drug in a vacuum.”
[ad_2]