[ad_1]

Additional waves of SARS-CoV-2 are anticipated as new variants unfold.Credit score: Dibyangshu Sarkar/AFP/Getty
Some name it a swarm of variants — others discuss with it as variant soup. No matter it’s known as, the present crop of immunity-dodging offshoots of the Omicron variant of SARS-CoV-2 is unprecedented in its range. This complexity makes it more durable to foretell coming waves of an infection. It’d even result in a ‘double wave’ in some locations, as first one variant after which one other overtakes a inhabitants.
However amid the chaos, patterns are rising. The swarm has helped scientists to pinpoint a handful of immunity-evading mutations that energy a variant’s unfold. Globally, a number of heavyweight variants have emerged, yielding completely different outcomes in several areas — at the very least, thus far.
In Europe, North America and Africa, the prevalence of Omicron offshoots within the BQ.1 household is rising shortly, whilst total circumstances appear to fall. In Asian international locations together with Singapore, Bangladesh and India, a lineage known as XBB has already set off contemporary waves of an infection. Scientists are carefully watching a number of areas the place each are circulating, to see which has the sting.
“Ultimately, most likely, some variants are going to dominate, nevertheless it’s much less decisive than it was prior to now,” says Cornelius Roemer, a computational biologist on the College of Basel in Switzerland.
One massive household
The variants which have pushed previous waves, similar to Alpha and Delta, all arose from distinct branches of the SARS-CoV-2 household tree. However since Omicron emerged in late 2021, it has spawned a sequence of subvariants, together with BA.2 and BA.5, which have sparked international waves of an infection. Many international locations put their BA.5-led surges within the rear-view mirror in mid-2022, however most scientists thought it was solely a matter of time earlier than one other sublineage got here to the fore.
For the previous few months, variant trackers have been combing by way of international SARS-CoV-2 sequencing information to establish candidates. However as an alternative of 1 or two fast-rising lineages, they’ve recognized greater than a dozen to observe.
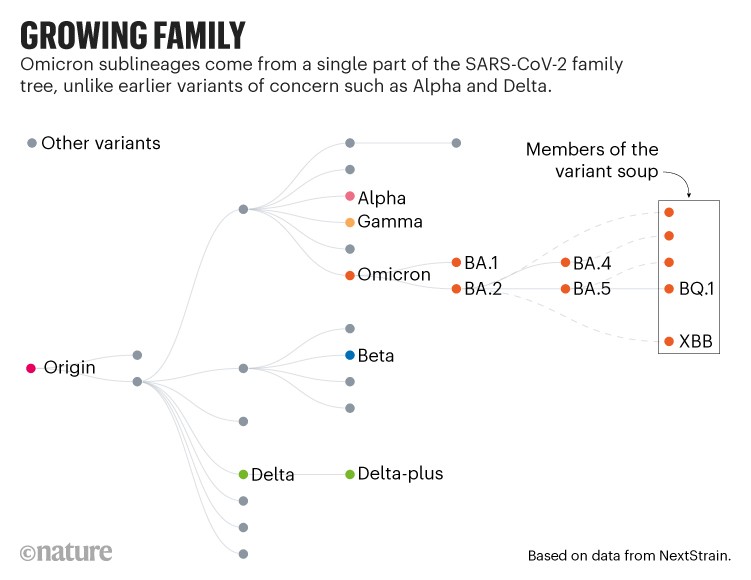
Supply: Nextstrain
“It’s a set or swarm or soup of variants collectively — not as now we have seen earlier than,” says Yunlong Richard Cao, an immunologist at Peking College in Beijing, whose workforce has been learning the variants’ immune-evading capacities.
The members of the swarm come from varied elements of the Omicron household tree. However their rise appears to be resulting from a handful of shared genetic mutations, most of which result in amino acid adjustments in a portion of the viral spike protein known as the receptor binding area (RBD). This a part of the protein is required to contaminate cells, and is the goal of antibodies that ship a potent immune response.
Work from Cao’s workforce this month1 means that the RBD mutations assist the virus to evade infection-blocking ‘neutralizing’ antibodies that had been triggered by COVID-19 vaccines and an infection with earlier Omicron offshoots, together with BA.2 and BA.5. (That work has not but been peer reviewed.)
Ringing the adjustments
Roemer and others have noticed that the extra of those RBD adjustments a variant possesses, the quicker it appears to develop, as measured by the variety of sequences reported to international databases. As an example, variants, similar to BQ.1,with 5 key RBD adjustments (relative to BA.2) appear to be rising in quantity at a slower fee than variants with six adjustments. A descendant of BQ.1 known as BQ.1.1 has six such adjustments, and is rising quickly throughout Europe, North America and different locations.
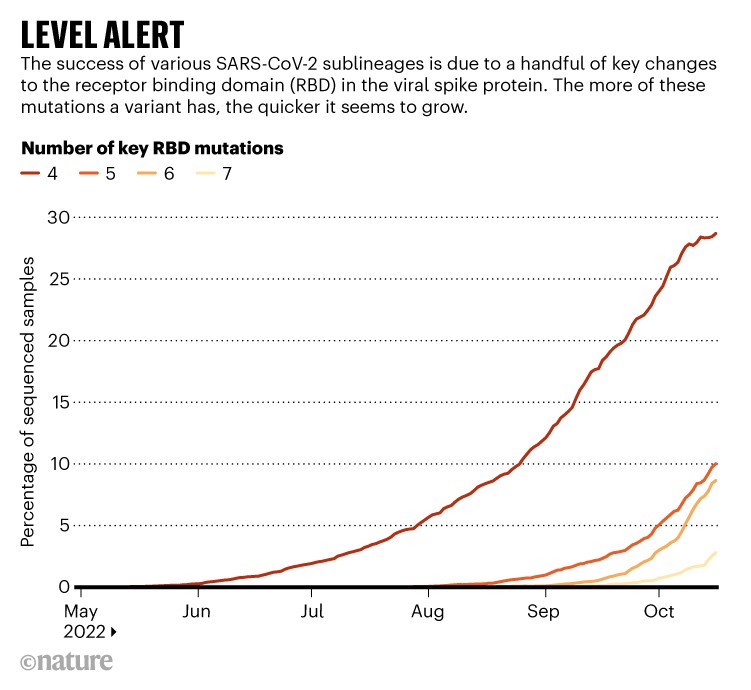
Supply: Cornelius Roemer, Cov-Spectrum.org and GISAID
A seventh RBD change appears to result in nonetheless swifter progress (though scientists warning that the estimates are approximate, notably when the variety of sequences recorded is small). The primary ‘degree 7’ variant scientists are monitoring is XBB. The sub-lineage is a hybrid, or recombinant, of two Omicron sublineages, each descendants of BA.2.
Of the swarm, BQ.1.1 and XBB appear to be rising to the highest. The BQ.1 household is already dominant in France and is more likely to drive an infection waves throughout Europe and North America as these areas enter winter. It’s also a typical ingredient of the variant soup in South Africa, Nigeria and elsewhere in Africa. XBB, against this, appears more likely to dominate infections in Asia, the place it not too long ago drove a wave of infections in Singapore.
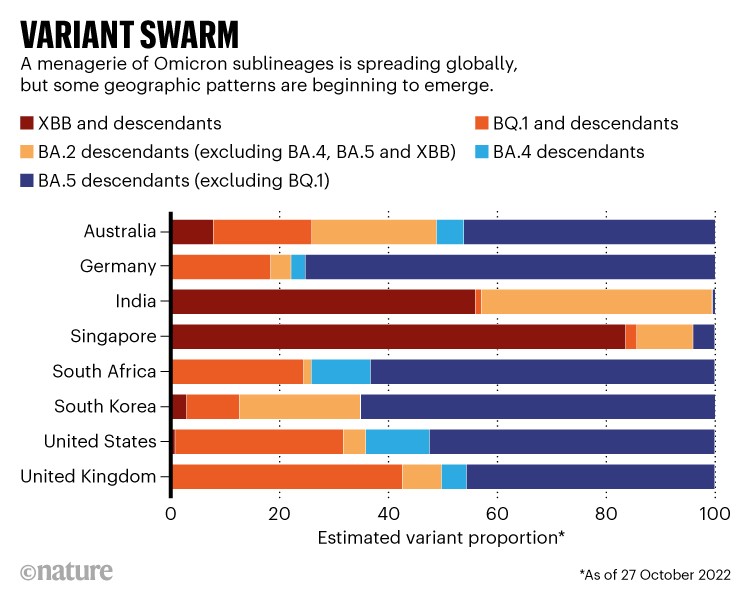
Supply: Moritz Gerstung, Cov-Spectrum.org and GISAID
Researchers are additionally monitoring international locations the place BQ.1.1 and XBB are co-circulating, to see which spreads quicker. In Australia, there are some early indicators that XBB is gaining an edge, notes Roemer. This additionally appears to be occurring in India, in keeping with Rajesh Karyakarte, a microbiologist primarily based on the BJ Authorities Medical Faculty in Pune, who coordinates SARS-CoV-2 genetic sequencing within the state of Maharashtra. “We might be ready to inform which one survives right here. We suspect XBB.”
What Omicron’s BA.4 and BA.5 variants imply for the pandemic
XBB’s benefit over the BQ.1 household may be due partly to adjustments exterior the spike RBD, says Cao. The variant additionally has mutations in a part of the genome encoding a area of the spike protein known as the N-terminal area (NTD). Our immune programs additionally goal this portion of spike with neutralizing antibodies, and individuals who have recovered from BA.2 and BA.5 infections mount particularly robust immune responses to NTD, in keeping with preliminary information from Cao’s lab.
XBB’s skill to dodge antibodies concentrating on the NTD would possibly enable it to contaminate individuals who had been proof against BQ.1 and its relations, Cao provides. However “BQ.1 is selecting up NTD mutations crazily quick”, he says. Unpublished work from his workforce means that such additions considerably improve these variant’s skill to evade neutralizing antibodies raised by vaccination and former an infection.
It’s doable that BQ.1.1 will trigger a spike in circumstances, just for XBB to overhaul it in some locations, says Roemer. “If it seems that XBB goes to dominate globally in the long run, we would see some kind of double wave in Europe and North America,” he says.
Double immunity?
A key determinant would be the extent to which an infection with BQ.1 lineages defend towards XBB. Cao’s workforce is at present engaged on this. “I’ve a sense that for those who’re contaminated with BQ.1, you might need some safety towards XBB,” he says. “We don’t have information but.”
Whether or not pushed by XBB, BQ.1.1 or one other member of the swarm, massive an infection waves can disrupt society, and even gentle infections would possibly end in long-lasting well being results. However researchers are preserving an particularly shut eye on whether or not the approaching waves result in excessive numbers of hospitalizations and deaths.
The hunt to seek out genes that drive extreme COVID
In an unpublished, preliminary examine of 28 individuals with XBB infections, Karyakarte’s workforce discovered that none had extreme signs. Karyakarte says his colleagues in Bangladesh report comparable patterns. Singapore has recorded a small rise in COVID-19 hospitalizations and deaths throughout its XBB wave, however these extreme results have been smaller than in previous waves.
However elements similar to seasonality — the Northern Hemisphere winter climate is probably going to provide SARS-CoV-2 circulation a lift — prior waves, and coverage imply that Singapore’s expertise may not predict what different international locations are in for, says Roemer. “It’s most likely not a blueprint for what’s going to occur.”
[ad_2]