[ad_1]

Dense smoke is pumped from a army tank’s exhaust pipe. Navy carbon dioxide emissions are big — and largely unaccounted for.Credit score: Stephen Barnes/Alamy
The world’s militaries are heavy emitters of greenhouse gases. Nobody is aware of precisely how a lot; estimates vary between 1% and 5% of worldwide emissions, comparable with the aviation and delivery industries (2% every). But militaries are largely spared from emissions reporting. This should change, or mitigation measures threat turning into mere guesswork1.
As an example, the US army is the world’s largest when it comes to expenditure. In the event that they had been a nation, US forces would have the best per-capita emissions on this planet, at 42 metric tonnes of carbon dioxide equal (CO2eq) per employees member (see ‘Navy emissions’). For every 100 nautical miles flown, the US Air Drive’s signature F-35 fighter jet emits as a lot CO2 (2.3 metric tonnes of CO2eq)2 as a mean UK petrol automotive pushed for one 12 months. Annually, jet-fuel use by the US army alone generates emissions equal to 6 million US passenger automobiles2.
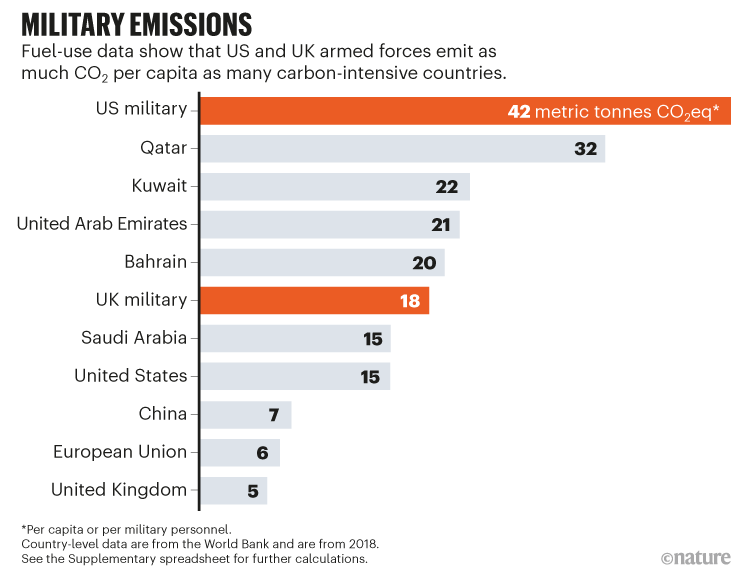
Supply: World Financial institution
Why are reviews from the Intergovernmental Panel on Local weather Change and United Nations local weather summits silent on army emissions? The quick reply is politics, and a lack of awareness. In the course of the 1997 Kyoto Protocol negotiations, US delegates lobbied on the grounds of nationwide safety to exclude the army from reporting necessities for greenhouse gases. That method has caught, though their argument not holds — strategies at the moment are accessible for counting emissions alongside international provide chains with out compromising intellectual-property rights or disclosing delicate info.
With no worldwide settlement on accountability, reporting necessities, management or will to behave, monitoring and slicing army emissions are low priorities. Solely a handful of forces — together with these of the United Kingdom and United States — have printed technique paperwork on local weather motion. Throughout the 27 member states of the European Union, we discovered solely ten militaries that had famous the necessity for greenhouse-gas mitigation, of which simply seven had set targets.
Additionally lacking are correct methodologies for calculating emissions from army actions. As for any massive enterprise, accessing emissions from the army’s everlasting websites and routine transport use is simple — however recording emissions is close to not possible in hostile, fast-changing or insecure places. A scarcity of printed information additionally makes it arduous to estimate totals for army emissons3.
Navy emissions should be placed on the worldwide agenda. They should be formally acknowledged and precisely reported in nationwide inventories, and army operations should be decarbonized. That requires greater than ‘greening’ army infrastructure or gear. A concerted effort is required to cut back army spending on carbon-intensive programmes and gear. Researchers have to develop clear frameworks for reporting army emissions, they usually should determine information gaps. The 2022 UN Local weather Change Convention of the Events in Sharm el-Sheikh, Egypt (COP 27), and the 2023 convention in Dubai, United Arab Emirates (COP 28), are alternatives to formalize this alteration.
Uncounted emissions
Reporting of army emissions below the UN Framework Conference on Local weather Change (UNFCCC) is incomplete, unclear and inconsistent (see go.nature.com/3eyzi). Some information have been shared on direct emissions from gas consumption, operation of services and consumed energy. Nonetheless, oblique emissions alongside provide chains are absent, and emissions calculations are sometimes flawed. Some figures may not be flagged as army in origin, and are categorised as an alternative below broader classes, akin to public buildings and providers or basic aviation or delivery.
The UK has among the finest monitor information in reporting its army carbon emissions. Since 2012, it has printed information for direct emissions within the annexes of Ministry of Defence (MOD) reviews. In 2018, as an example, British forces emitted round 2.7 million metric tonnes of CO2eq4, roughly equal to emissions from 1.5 million UK automobiles.

Sailors aboard a US Navy cruiser observe a gas probe aboard a assist ship coming to refuel their vessel at sea.Credit score: Nelly George/Alamy
But, within the figures reported to the UNFCCC in 2019, solely 64% of the MOD’s declared emissions had been explicitly recognized as belonging to the army — these referring to army plane and naval vessels. It’s unclear how emissions from army bases and floor autos had been reported. Additional analysis may test whether or not such emissions had been listed below civilian classes. Additionally unclear is whether or not all bunker fuels used for worldwide army transport had been included.
Reporting in different international locations may be much more scattershot. In america, information of direct army emissions are positioned throughout authorities departments, and are sometimes opaque owing to ‘nationwide safety issues’. One estimate means that actions of the US Division of Protection (DOD) — together with all branches of the US armed forces and their civilian assist employees — launched 55.4 million metric tonnes of CO2eq in 2018 (see go.nature.com/3waw9), roughly equal to the emissions of 12 million US automobiles. Greenhouse-gas emissions from the US army exceed these of many international locations, together with Switzerland, Ghana and New Zealand. Have been the US DOD a nation, it could be the 54th highest emitter globally (see Supplementary Info).
Scant information can be found from different nations with massive armed forces. These embody Russia, which is at the moment waging battle with Ukraine, and China and India, which have extra energetic army personnel than does america. Speedy development for the most important army energy, China, with its two million energetic personnel, may be anticipated: earlier this month, President Xi Jinping introduced that the nation intends to have a ‘world-class army’ by 2049.
Different international locations, akin to Peru, Indonesia and South Africa, don’t have to report their nationwide emissions yearly, as a result of UNFCCC obligations differ in keeping with ranges of financial growth. As rising economies are sometimes carbon-intensive, their army emissions could be much more important than these we learn about or can estimate.
Analyses of fossil-fuel consumption recommend that the world’s militaries might emit round 0.45 billion to 2.2 billion metric tonnes of CO2eq yearly5. The true whole could be even larger: factoring in different emissions from power provides, uncooked supplies, provide chains and gear manufacturing might greater than triple estimates6. Emissions from warfare would add extra5, however are troublesome to measure. Gas consumption through the Iraq battle may need launched greater than 250 million metric tonnes of CO2eq between 2003 and 2011, greater than the annual emissions of many international locations5.
Monitoring and reporting
No methodologies for monitoring emissions on army bases or in battle areas have been printed. The North Atlantic Treaty Group (NATO) is reportedly growing such a framework for its members; little is thought publicly about its methodology, robustness and applicability7. We anticipate that supply-chain emissions or emissions from armed conflicts will go unaddressed.
A standardized methodology and complete evaluation framework for greenhouse-gas emissions, together with these embedded in merchandise throughout their life cycles, are wanted. Though a lot may be drawn from different industries, military-specific environments and circumstances should be thought-about.

A NASA plane trails an airliner as a part of exams sampling emissions from low-carbon fuels.Credit score: NASA/eyevine
There are two main gaps. First, the day-to-day footprint of militaries themselves should embody the emissions related to the administration of bases and estates — from offering infrastructure, cement and meals to feed and home the troops. Second, a reckoning is required on the impacts of infrastructure harm, land-use modifications, socio-economic shifts and post-war reconstruction and restoration8. Regardless of twenty years of progress on documenting the environmental dimensions of armed conflicts, efforts to calculate these emissions are of their infancy.
Russia’s battle in Ukraine has drawn contemporary consideration to the function of fossil fuels in financing conflicts, as a goal and as a device for political coercion. The Ukrainian authorities is calculating the monetary and environmental prices of the impression of the battle on the local weather — the primary time that any conflict-affected state has performed so — which will likely be raised at COP27.
Analysis areas that want funding embody strategies for independently verifying military-emissions accounting by third events, together with teachers and civil society teams, with out compromising nationwide safety. Breaking down emissions by expertise sectors will assist to prioritize actions and targets. Research on the feasibility of adopting low-carbon applied sciences are key. Software program that creates a barcode that may be scanned to disclose a product’s emissions information could be useful; that is already used within the non-public sector to trace emissions all through a provide chain, for instance in meals and agriculture initiatives. Such information can inform declarations of emissions for processes, services or products9.
Decarbonizing operations
As soon as reporting mechanisms are in place, plans for decarbonizing the army should be assessed and improved. Militaries will want assist from researchers to do that successfully. One main problem is ‘lock in’ — emissions from army gear are mounted for many years, owing to lengthy procurement processes and lifespans. For instance, F-16 fighter planes entered service with the US Air Drive in 1979, and will not be as a result of be retired till about 2040. Regardless of proposals to impress land autos, and to advertise artificial fuels for aviation10, fossil-fuel use in international militaries will proceed to rise for a few years to come back.
Warships, fight plane and floor autos should develop into extra gas environment friendly and make the most of renewables (see ‘Federal power consumption’). For reconnaissance, light-weight craft, akin to drones, and satellite tv for pc information must be used extra usually. Photo voltaic photovoltaic arrays and electrical autos ought to develop into the norm on army bases. The UK’s MOD and its Defence Innovation Fund concepts scheme, the ViTAL Residing Lab, develop and harness photo voltaic, geothermal, hydrogen and electrical power to be used on the Royal Air Drive’s Leeming base as a testbed.
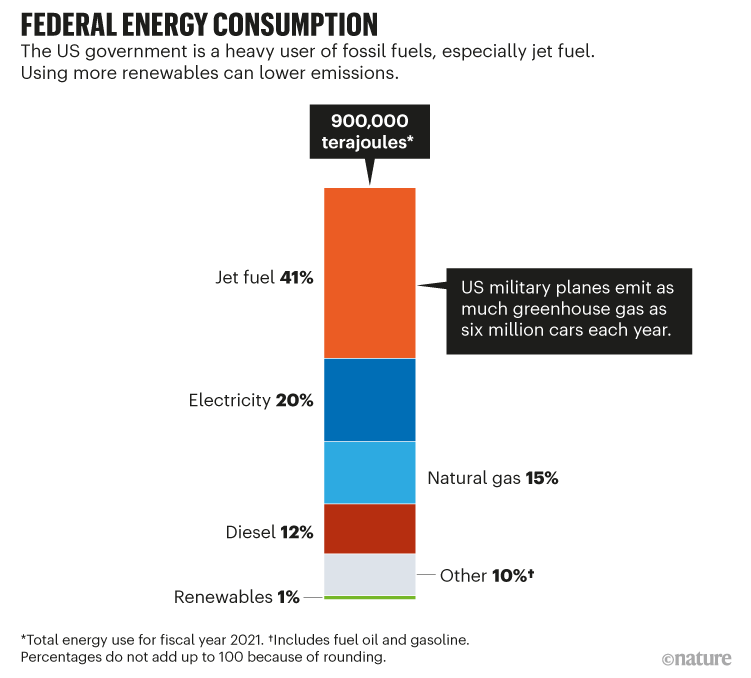
Supply: US Division of Power
Life-cycle impacts and raw-material necessities are one other black field9. There may very well be unintended penalties when switching to different applied sciences. For some applied sciences, akin to lithium-ion batteries, massive quantities of power — and subsequent emissions — are required within the provide chain. Utilizing a brand new expertise may improve reliance on uncommon uncooked supplies, akin to cobalt or antimony.
The supplies which might be required in wartime might differ from these wanted in on a regular basis civilian environments. As an example, analysis funding is required into low-carbon supplies with robust anti-blast properties in lieu of concrete. Navy innovation may confer some advantages to the civilian sector. New constructing supplies, photovoltaics and new energy sources could be helpful the place power is quickly unavailable, akin to in disaster-relief operations.
Navy bases additionally want to deal with local weather extremes, akin to storm-surge flooding, wind, wildfire and drought. The US DOD oversees greater than 1,700 worldwide army services on coastlines that may very well be weak to sea-level rise, in keeping with the Congressional Analysis Service. A departmental survey (see go.nature.com/3uzh7) in 2019 on 79 installations concluded that almost two-thirds of them are in danger from recurring flooding, and one-half face threats from drought or wildfires.
All this wants to maneuver past plans and high-level discussions which might be a part of diplomatic efforts, arms-control treaties and different conflict-prevention measures. Crucially, global-security enhancements result in reductions in worldwide army expenditure and its related emissions. For instance, after the top of the chilly battle, army emissions throughout NATO members and the Soviet bloc fell markedly between 1991 and 2000. Whole US army emissions declined by 44%2.
Subsequent steps
We name for motion in 4 areas.
First, militaries throughout the globe should be held accountable. Though nationwide net-zero pledges have helped to focus consideration in some international locations, worldwide requirements and obligations should be agreed. The UNFCCC is essentially the most applicable discussion board and should strengthen and reform its reporting protocols to incorporate militaries. COP27 and COP28 are key alternatives for these states which have already engaged on the military-emissions agenda, akin to america and United Kingdom, to point out management. Researchers should advocate for frequent requirements for accounting, reporting and lowering army emissions, and these should be clear, time-bound and measurable.
Second, militaries should enhance their capability to calculate, handle and scale back emissions, and prepare personnel to take action. Researchers ought to work with the armed forces to alternate data and greatest practices from the civil sector; assist to develop protocols for military-specific emissions; and use or procure low-carbon gear.
Third, researchers have to doc and perceive how armed conflicts impression the local weather and society. This dynamic is advanced however essential for figuring out low-carbon restoration pathways for international locations coming into battle, akin to Ukraine, and for understanding the long-range prices of armed battle. Lastly, unbiased analysis is paramount to maintain militaries accountable and to uphold obligations made below the UNFCCC. Clearly, there may be an pressing want to offer researchers the assist to conduct unbiased analyses and supply evidence-based options, and militaries ought to work hand in hand with academia and trade to ascertain a generally understood and verifiable technique of emissions accounting.
[ad_2]
