[ad_1]
Lengthy-read techniques make it simpler to assign a given sequence to a chromosome copy.Credit score: SCIEPRO/Getty
The phrase ‘reference’ conveys authority, signifying a trusted useful resource in opposition to which new info can confidently be assessed. That was true of encyclopaedias and atlases, and it’s true of reference genomes — ultra-high-accuracy maps that describe the entire sequence of a species’ chromosomal DNA.
But it surely’s an open secret that particular person reference genomes do a poor job of offering real-world organic blueprints. David Edwards, a bioinformatician on the College of Western Australia in Perth, remembers a colleague who wished to review gene expression in wheat variants utilizing a single, well-studied pressure. “We’ve proven that there’s like 20,000 genes which can be in industrial wheat strains however are usually not in that reference,” he says. “You’re lacking an enormous quantity except you’re taking account of that.”
With extremely advanced and variable genomes, vegetation are an excessive instance, however hidden range is all over the place. One comparability of 64 genomes of human people revealed practically 16 million single-nucleotide variations and greater than 2 million structural variants through which sequences have been deleted or inserted1. This makes it unimaginable to outline anybody genome as ‘the reference’ in opposition to which all others may be in contrast. And, given that almost all genomes sequenced thus far are from folks of western European descent, key genomic insights for people of different backgrounds might be missed. “It’s sort of a nightmare to check a genomic drugs observe that might work higher for folks of some ancestries and worse for folks of different ancestries,” says Tobias Marschall, a computational-genomics researcher at Heinrich Heine College in Düsseldorf, Germany, and a lead creator of that comparability research.
The answer is the pangenome: a composite reference, made out of a number of genomes, that captures a wider vary of variability and variety at any given chromosomal website. Already a longtime device for microbes and vegetation, pangenomes are lastly reaching the vertebrate world. In July 2022, the Human Pangenome Reference Consortium (HPRC) revealed a preprint of a draft pangenome primarily based on 47 people who signify a large swathe of ethnic and geographic range2. A whole lot extra genomes are actually slated for incorporation into this meeting.
However pangenomes are nonetheless new sufficient that the sphere is grappling with the way to bundle and discover them — and to influence researchers to discard the acquainted linear references of typical genomics. “That is one thing that may take the entire discipline a couple of decade to transition,” predicts Benedict Paten, a computational-genomics researcher on the College of California, Santa Cruz (UCSC), and a part of the HPRC. “You’ve received to exhibit that it really improves issues for folks — in any other case, what’s the purpose?”
I comprise multitudes
As with so many genetics advances, the earliest demonstrations of pangenomics got here from single-cell microbes. In 2005, a group led by Claire Fraser on the Institute for Genomic Analysis in Rockville, Maryland, and Rino Rappuoli at Chiron Vaccines in Siena, Italy, created an meeting of genomes from eight isolates of Streptococcus agalactiae, a bacterium chargeable for probably deadly infections in younger youngsters3. Every added genome introduced dozens of latest genes into the meeting — which they known as a ‘pan-genome’ (‘pan’ being Greek for ‘complete’) — starkly highlighting the shortcomings of typical references.
Closing in on an entire human genome
Microbial pangenomics is now a thriving space of analysis. Bernhard Palsson, a techniques biologist on the College of California, San Diego, says that by 2013, his group had compiled 55 totally different strains of Escherichia coli into one pangenome4. By assessing how variants throughout genomes correlate with organic capabilities in these micro organism, they have been capable of hyperlink variations in metabolism and virulence to particular genes and chromosomal options. Since then, Palsson’s group has pushed the pangenome idea past the pressure and species stage to survey much more distantly associated organisms, together with a household of micro organism generally known as Lactobacillaceae. “We had 3,500 genomes or so to work with,” he says.
The primary eukaryotic pangenomes got here from the plant world, beginning with the meeting, in 2014, of seven soya-bean genomes by a bunch led by crop geneticist Lijuan Qiu on the Chinese language Academy of Agricultural Sciences in Beijing5. Essential crops resembling wheat, maize (corn) and rice adopted. “A lot of the main species now have pangenomes,” says Jacqueline Batley, a plant-genomics researcher on the College of Western Australia and a detailed collaborator of Edwards’s. Plant biologists are utilizing these sources to develop improved variants that incorporate genetic options related to hardiness in opposition to drought or pathogens, elevated yield and different useful traits.
Progress within the human pangenome realm has been propelled by improvements in sequencing and genome meeting that allowed a community of researchers throughout the globe to publish the primary really full ‘telomere-to-telomere’ genome sequence6 in March 2022. Karen Miga, the UCSC geneticist who co-led this effort, says the completion in 2019 of the primary full human X chromosome sequence — with its messy assortment of extremely repetitive parts — was like “taking pictures a flare gun up into the air”, signalling that the group lastly had the capability to pursue a human pangenome reference. “It was only a matter of determining the suitable data-production and meeting technique,” she says. The HPRC — for which Miga is a programme director — was launched that very same yr.
A sequence of advances
For the primary wave of pangenomes, DNA sequences have been largely collected utilizing ‘short-read’ techniques developed by biotechnology agency Illumina, primarily based in San Diego, California, that are extremely correct however produce reads which can be solely about 100–200 nucleotides lengthy. Researchers can assemble these fragments into ‘contigs’ that reveal comparatively small variations resembling single-nucleotide variants and ‘indels’ — insertions or deletions of a handful of nucleotides — however that can’t resolve bigger structural variations. For that reason, early pangenomes sometimes mapped short-read-derived contigs from every specimen to an present reference. This strategy tends to supply gene-centric pangenomes that miss advanced structural variation in particular person genomes, which may play an necessary half in gene regulation and comprise important details about genome evolution.
Lengthy street to long-read meeting
Nonetheless, these ‘map-to-pangenome’ approaches may be helpful. Edwards and Batley say that their first try at a wheat pangenome primarily based on short-read evaluation, in 2017, was extremely efficient for figuring out which genes are absent or current particularly cultivars7. However this strategy additionally undermines the entire function of making a reference, by introducing biases on the premise of which genome serves because the pangenome’s basis, such that one meeting might differ significantly from one other.
A greater answer is to construct a number of reference-quality genomes and align these in an unbiased trend, charting the place they match and the way they differ — an strategy made possible by the speedy evolution of ‘long-read’ sequencing applied sciences.
Longer reads have additionally simplified a second, thorny problem. People — and lots of plant and animal species — are diploid, which means that they carry two copies of each non-sex chromosome. Every copy has its personal sample of variations, generally known as a haplotype. Some species have greater than two copies; wheat, as an illustration, accommodates six. This presents a baffling downside for short-read sequencing — the way to assign a given learn to a selected chromosome copy. “It’s like placing two big puzzles collectively, and the items are so comparable, you don’t know which one it goes to,” says Erich Jarvis, a neurogenetics researcher on the Rockefeller College in New York Metropolis. This, he provides, represents “one of many largest issues to getting correct genome assemblies”.
Going by means of a part
For the HPRC’s ‘first draft’ pangenome, Jarvis, Miga and their colleagues tackled the haplotype downside by utilizing genome knowledge from every DNA donor’s mother and father, giving perception into which units of variants got here from the mom and which from the daddy8. Lengthy-read sequencing was important right here, as a result of it allowed HPRC scientists to traverse sufficiently huge stretches of DNA to differentiate one chromosome from the opposite. By feeding the information from all three genomes right into a software program device known as Hifiasm, the researchers have been capable of get better diploid genomes for which every chromosome’s haplotype was successfully resolved, or ‘phased’.
Nonetheless, the 47 diploid genomes on this preliminary pangenome are usually not full assemblies just like the telomere-to-telomere genome. That effort exploited an uncommon cell line through which each chromosome copies are similar. In true diploid cells, Jarvis says, the HPRC workflow sometimes yields not a single chromosome however lots of of large contigs, with gaps occurring in arrays of ultra-similar duplicated genes in addition to the gnarly and repetitive centromeric areas that join every chromosome’s gene-laden arms. The consortium remains to be fighting how finest to deal with these problematic areas, he says.
Seven applied sciences to observe in 2022
The excellent news is that the present course of covers the vast majority of the genome and may be largely automated. Marschall highlights Verkko, software program developed by his former scholar Mikko Rautiainen whereas he was a postdoc on the US Nationwide Human Genome Analysis Institute in Bethesda, Maryland, that vastly simplifies diploid meeting. “Some chromosomes come again simply in a single, totally phased contig,” he says. That ought to assist the HPRC to satisfy its objective of assembling 350 various genomes for the first-generation human pangenome by 2024.
Consortium scientists have additionally recognized experimental strategies that permit them to bodily hyperlink collectively sequencing reads that originate from the identical chromosome — even over very lengthy distances — eliminating the burdensome requirement of accumulating and sequencing parental DNA. “I believe now we’re at some extent the place we will virtually get telomere-to-telomere [assemblies] within the diploid setting with single samples,” says Marschall.
This leaves the important query of the way to depict a pangenome. The linear maps used as an instance reference genomes over the previous 20 years don’t work for assemblies comprising tens, lots of and even 1000’s of particular person genomes.
Most researchers within the discipline have converged on graph pangenomes as one of the best present answer to this downside (see ‘Visualizing a Pangenome’). These elaborate community diagrams collapse shared areas of genome sequence to the acquainted flat line, however loop out into divergent paths at websites the place variability can happen. Consider a metropolis public-transport map, which presents default routes for trains. Upkeep, accidents or rush-hour schedules may cause trains to reroute on to different strains or skip stations, however there are limits on the variety of detours. A graph-style map of the prepare line would seize each the invariant elements of a route and all detours which have been recognized to happen — basically, describing the vary of doable haplotypes for that line.
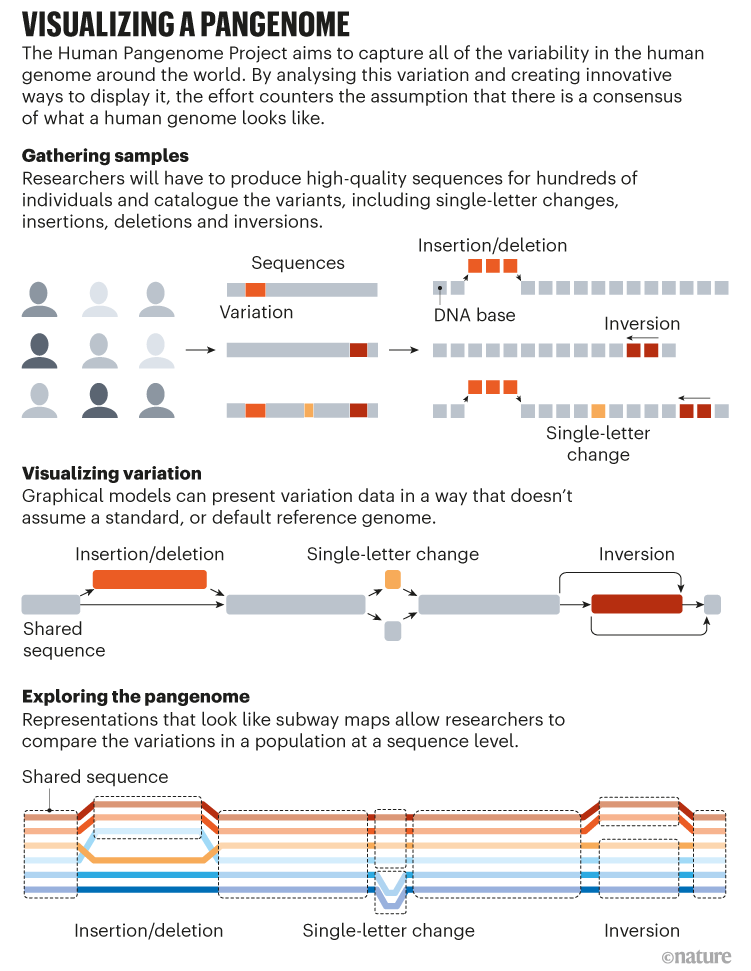
Computational-genomics researchers are nonetheless understanding how finest to construct such graphs, and the HPRC’s draft-pangenome preprint explores a number of potentialities. One entails iterative meeting of particular person diploid genomes, however though that strategy might deal with giant structural variations properly, “it didn’t carry base-level decision”, Miga says. The opposite, extra computationally intensive strategy entails aligning all genomes concurrently, which works effectively for gene-containing areas however struggles in repetitive, low-complexity chromosomal areas. “That’s why, deliberately, this paper has ‘draft’ within the title, to convey that it’s our first shot,” says Marschall.
Researchers constructing non-human pangenomes face steeper challenges. Edwards and Batley have discovered that human-centric graph-assembly software program packages don’t work so effectively with vegetation, as an illustration. “We want some extra instruments,” says Edwards, noting that the better complexity of plant genomes relative to human ones represents an important stumbling block. And Jarvis, who can also be coordinating the Vertebrate Genomes Venture, an initiative to construct reference sequences for each vertebrate species on Earth, says the HPRC’s pipelines translate poorly to lots of our animal family members. “Even for this human pangenome, we’re discovering that the meeting instruments should be tweaked somewhat bit extra for various folks,” says Jarvis.
There may be additionally the problem of getting the broader group on board. Previous iterations of the human reference genome have been gradual to percolate into common utilization, and lots of medical laboratories nonetheless haven’t adopted the present state-of-the-art reference, GRCh38. Plus, researchers exterior the sphere would possibly discover this new reference format off-putting. “Individuals are daunted by the graphs,” says Batley.
One answer is to construct instruments that maintain the graph itself ‘beneath the hood’, and let researchers interrogate particular areas of the genome with extra user-friendly graphical interfaces. Miga champions the thought of linking the human pangenome to GRCh38 sequence coordinates in order that customers of the present reference don’t want to totally overhaul their analytical workflows. However selling graph pangenome uptake shall be a high precedence for the HPRC within the coming yr, she provides.
A brand new body of reference
In the end, one of the best commercial for pangenomes shall be proof of their energy, and pioneers within the discipline are enthusiastic in regards to the secrets and techniques {that a} well-assembled multi-genome reference can unlock.
NatureTech hub
Once more, microbial pangenomics is main the best way. Palsson factors to a 2018 evaluation of haplotype-specific traits that his group performed utilizing a pangenome comprising practically 1,600 isolates of Mycobacterium tuberculosis9, the bacterium that causes tuberculosis. “We might affiliate that [genomic variability] with metabolic properties and elucidate antimicrobial-resistance mechanisms,” he says.
Equally, plant pangenomes are serving to researchers to house in on beforehand neglected genes that confer a survival edge in harsh circumstances. Zhixi Tian, a plant genomicist on the Chinese language Academy of Sciences in Beijing, notes that many of those options reside in structurally variable areas that have been absent from earlier reference genomes. “Often for the stress-related traits, the genes that management them are duplicated,” says Tian. “The dosage distinction makes the trait distinction.”
Pangenome maps might show equally highly effective for uncovering the hidden variation that underlies advanced developmental and medical circumstances in people. For instance, the Paten group’s Giraffe algorithm can analyse hundreds of thousands of tiny snippets of the short-read sequencing knowledge that’s sometimes collected in medical genomics and extrapolate which haplotype ‘route’ somebody’s sequence follows by means of the graph, filling within the blanks about the remainder of their genome. Jarvis additionally cites the potential for creating centered pangenomes for medical and developmental circumstances, resembling autism spectrum dysfunction, after which evaluating these in opposition to the baseline pangenome to establish divergent genomic options.
One other thrilling chance is integrating pangenome references with different organic info to supply a extra holistic view of how chromosomal variation informs mobile operate. For instance, some researchers are creating ‘pantranscriptomic’ knowledge units that complement genomic knowledge with RNA sequencing to review how DNA variation influences the amount and construction of the ensuing gene transcripts. And the HPRC group is accumulating epigenetic knowledge from its donor genomes to higher perceive the molecular-scale variations in gene expression between people.
“It’s not about simply the bottom pairs,” Miga emphasizes. “We have to begin constructing that kind of annotation map on high of the pangenome, so it turns into a one-stop store.”
[ad_2]