[ad_1]
The core protocol of the Web, aptly named the
Web Protocol (IP), defines an addressing scheme that computer systems use to speak with each other. This scheme assigns addresses to particular gadgets—individuals’s computer systems in addition to servers—and makes use of these addresses to ship knowledge between them as wanted.
It’s a mannequin that works properly for sending distinctive data from one level to a different, say, your financial institution assertion or a letter from a beloved one. This strategy made sense when the Web was used primarily to ship completely different content material to completely different individuals. However this design isn’t properly suited to the mass consumption of static content material, corresponding to films or TV reveals.
The fact at this time is that the Web is extra usually used to ship precisely the identical factor to many individuals, and it’s doing an enormous quantity of that now, a lot of which is within the type of video. The calls for develop even greater as our screens get hold of ever-increasing resolutions, with 4K video already in widespread use and 8K on the horizon.
The
content material supply networks (CDNs) utilized by streaming providers corresponding to Netflix assist tackle the issue by briefly storing content material near, and even inside, many ISPs. However this technique depends on ISPs and CDNs having the ability to make offers and deploy the required infrastructure. And it may well nonetheless go away the perimeters of the community having to deal with extra site visitors than truly must movement.
The true downside isn’t a lot the quantity of content material being handed round—it’s how it’s being delivered, from a central supply to many various far-away customers, even when these customers are situated proper subsequent to 1 one other.
A extra environment friendly distribution scheme in that case can be for the information to be served to your system out of your neighbor’s system in a direct peer-to-peer method. However how would your system even know whom to ask? Welcome to the InterPlanetary File System (IPFS).
The InterPlanetary File System will get its identify as a result of, in concept, it could possibly be prolonged to share knowledge even between computer systems on completely different planets of the photo voltaic system. For now, although, we’re targeted on rolling it out for simply Earth!
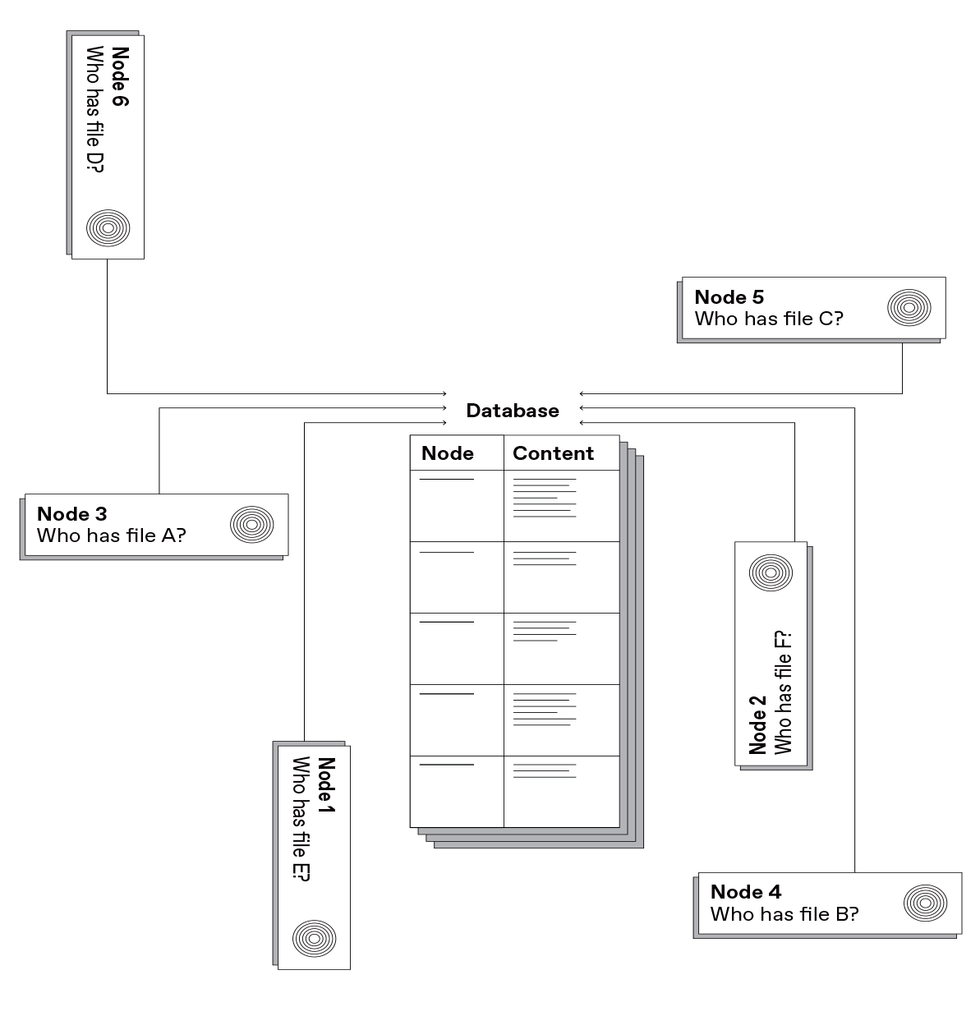
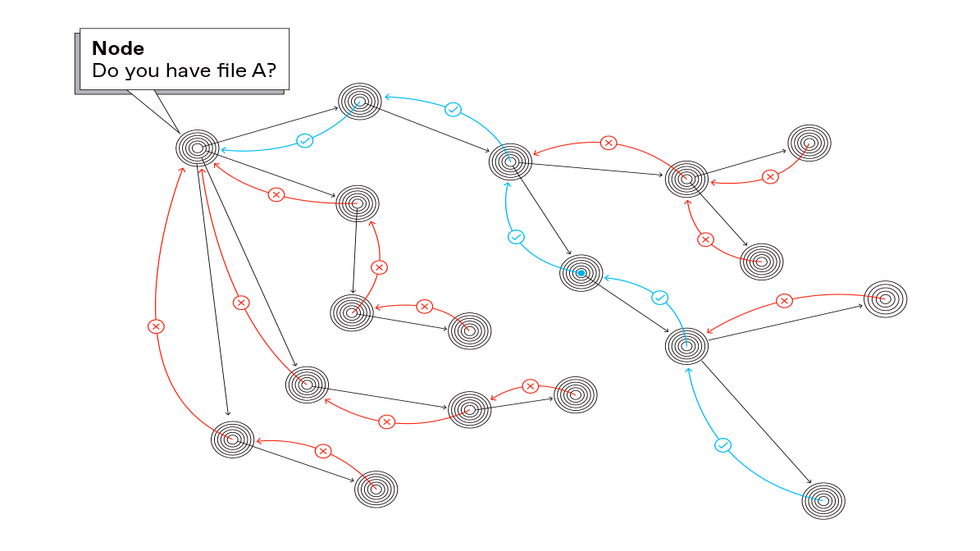
The important thing to IPFS is what’s referred to as content material addressing. As an alternative of asking a specific supplier, “Please ship me this file,” your machine asks the community, “Who can ship me this file?” It begins by querying friends: different computer systems within the person’s neighborhood, others in the identical home or workplace, others in the identical neighborhood, others in the identical metropolis—increasing progressively outward to globally distant places, if want be, till the system finds a duplicate of what you’re in search of.
These queries are made utilizing IPFS, an alternative choice to the
Hypertext Switch Protocol (HTTP), which powers the World Extensive Net. Constructing on the rules of peer-to-peer networking and content-based addressing, IPFS permits for a decentralized and distributed community for knowledge storage and supply.
The advantages of IPFS embrace quicker and more-efficient distribution of content material. However they don’t cease there. IPFS also can enhance safety with content-integrity checking in order that knowledge can’t be tampered with by middleman actors. And with IPFS, the community can proceed working even when the connection to the originating server is lower or if the service that originally offered the content material is experiencing an outage—significantly essential in locations with networks that work solely intermittently. IPFS additionally provides resistance to censorship.
To know extra totally how IPFS differs from most of what takes place on-line at this time, let’s take a fast take a look at the Web’s structure and a few earlier peer-to-peer approaches.
As talked about above, with at this time’s Web structure, you request content material based mostly on a server’s tackle. This comes from the protocol that underlies the Web and governs how knowledge flows from level to level, a scheme first described by Vint Cerf and Bob Kahn in a 1974 paper within the IEEE Transactions on Communications and now referred to as the Web Protocol. The World Extensive Net is constructed on prime of the Web Protocol. Looking the Net consists of asking a particular machine, recognized by an IP tackle, for a given piece of knowledge.
As an alternative of asking a specific supplier, “Please ship me this file,” your machine asks the community, “Who can ship me this file?”
The method begins when a person varieties a URL into the tackle bar of the browser, which takes the hostname portion and sends it to a
Area Title System (DNS) server. That DNS server returns a corresponding numerical IP tackle. The person’s browser will then connect with the IP tackle and ask for the Net web page situated at that URL.
In different phrases, even when a pc in the identical constructing has a duplicate of the specified knowledge, it should neither see the request, nor wouldn’t it be capable to match it to the copy it holds as a result of the content material doesn’t have an intrinsic identifier—it isn’t content-addressed.
A content-addressing mannequin for the Web would give knowledge, not gadgets, the main position. Requesters would ask for the content material explicitly, utilizing a singular identifier (akin to the
DOI quantity of a journal article or the ISBN of a e book), and the Web would deal with forwarding the request to an accessible peer that has a duplicate.
The key problem in doing so is that it could require modifications to the core Web infrastructure, which is owned and operated by 1000’s of ISPs worldwide, with no central authority in a position to management what all of them do. Whereas this distributed structure is without doubt one of the Web’s biggest strengths, it makes it almost inconceivable to make basic modifications to the system, which might then break issues for most of the individuals utilizing it. It’s usually very laborious even to implement incremental enhancements. A great instance of the issue encountered when introducing change is
IPv6, which expands the variety of doable IP addresses. At the moment, virtually 25 years after its introduction, it nonetheless hasn’t reached 50 % adoption.
A manner round this inertia is to implement modifications at the next layer of abstraction, on prime of present Web protocols, requiring no modification to the underlying networking software program stacks or intermediate gadgets.
Different peer-to-peer techniques apart from IPFS, corresponding to
BitTorrent and Freenet, have tried to do that by introducing techniques that may function in parallel with the World Extensive Net, albeit usually with Net interfaces. For instance, you’ll be able to click on on a Net hyperlink for the BitTorrent tracker related to a file, however this course of sometimes requires that the tracker knowledge be handed off to a separate utility out of your Net browser to deal with the transfers. And when you can’t discover a tracker hyperlink, you’ll be able to’t discover the information.
Freenet additionally makes use of a distributed peer-to-peer system to retailer content material, which could be requested through an identifier and may even be accessed utilizing the Net’s HTTP protocol. However Freenet and IPFS have completely different goals: Freenet has a powerful concentrate on anonymity and manages the replication of knowledge in ways in which serve that purpose however reduce efficiency and person management. IPFS supplies versatile, high-performance sharing and retrieval mechanisms however retains management over knowledge within the fingers of the customers.
We designed IPFS as a protocol to improve the Net and to not create an alternate model. It’s designed to make the Net higher, to permit individuals to work offline, to make hyperlinks everlasting, to be quicker and safer, and to make it as straightforward as doable to make use of.
IPFS began in 2013 as an open-source mission supported by Protocol Labs, the place we work, and constructed by a vibrant group and ecosystem with lots of of organizations and 1000’s of builders. IPFS is constructed on a powerful basis of earlier work in peer-to-peer (P2P) networking and content-based addressing.
The core tenet of all P2P techniques is that customers concurrently take part as purchasers (which request and obtain recordsdata from others)
and as servers (which retailer and ship recordsdata to others). The mixture of content material addressing and P2P supplies the best substances for fetching knowledge from the closest peer that holds a duplicate of what’s desired—or extra accurately, the closest one by way of community topology, although not essentially in bodily distance.
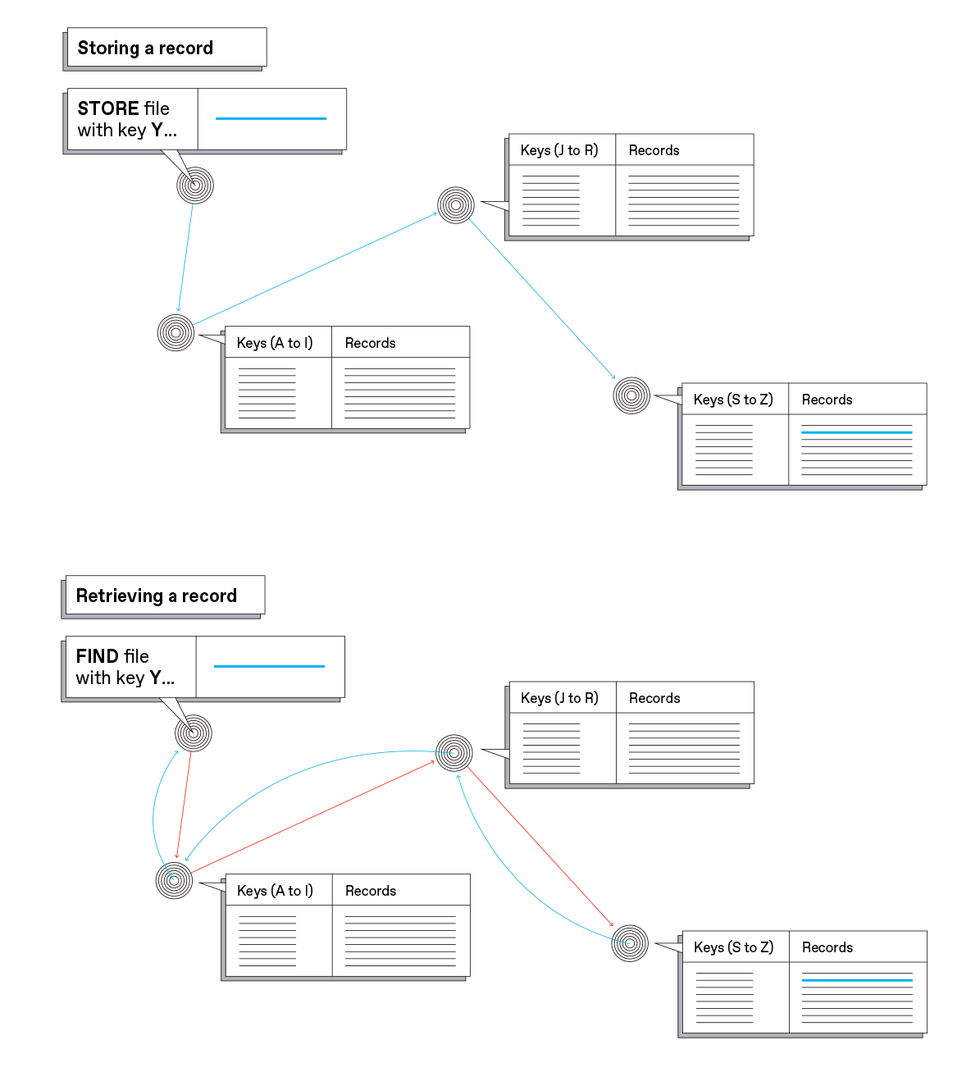
To make this occur, IPFS produces a fingerprint of the content material it holds (referred to as a
hash) that no different merchandise can have. That hash could be regarded as a singular tackle for that piece of content material. Altering a single bit in that content material will yield a completely completely different tackle. Computer systems eager to fetch this piece of content material broadcast a request for a file with this explicit hash.
As a result of identifiers are distinctive and by no means change, individuals usually consult with IPFS because the “Everlasting Net.” And with identifiers that by no means change, the community will be capable to discover a particular file so long as some pc on the community shops it.
Title persistence and immutability inherently present one other important property: verifiability. Having the content material and its identifier, a person can confirm that what was obtained is what was requested for and has not been tampered with, both in transit or by the supplier. This not solely improves safety but additionally helps safeguard the general public file and stop historical past from being rewritten.
You would possibly marvel what would occur with content material that must be up to date to incorporate recent data, corresponding to a Net web page. This can be a legitimate concern and IPFS does have a set of mechanisms that might level customers to probably the most up-to-date content material.
Decreasing the duplication of knowledge shifting by way of the community and procuring it from close by sources will let ISPs present quicker service at decrease price.
The world had an opportunity to look at how content material addressing labored in April 2017 when the federal government of Turkey
blocked entry to Wikipedia as a result of an article on the platform described Turkey as a state that sponsored terrorism. Inside per week, a full copy of the Turkish model of Wikipedia was added to IPFS, and it remained accessible to individuals within the nation for the almost three years that the ban continued.
An identical demonstration passed off half a 12 months later, when the Spanish authorities tried to suppress an independence referendum in Catalonia, ordering ISPs to dam associated web sites. As soon as once more, the knowledge
remained accessible through IPFS.
IPFS is an open, permissionless community: Any person can be part of and fetch or present content material. Regardless of quite a few open-source success tales, the present Web is closely based mostly on closed platforms, a lot of which undertake lock-in ways but additionally provide customers nice comfort. Whereas IPFS can present improved effectivity, privateness, and safety, giving this decentralized platform the extent of usability that persons are accustomed to stays a problem.
You see, the peer-to-peer, unstructured nature of IPFS is each a energy and a weak spot. Whereas CDNs have constructed sprawling infrastructure and superior methods to supply high-quality service, IPFS nodes are operated by finish customers. The community due to this fact depends on their habits—how lengthy their computer systems are on-line, how good their connectivity is, and what knowledge they determine to cache. And sometimes these issues will not be optimum.
One of many key analysis questions for the parents working at Protocol Labs is learn how to hold the IPFS community resilient regardless of shortcomings within the nodes that make it up—and even when these nodes exhibit egocentric or malicious habits. We’ll want to beat such points if we’re to maintain the efficiency of IPFS aggressive with standard distribution channels.
You might have observed that we haven’t but offered an instance of an IPFS tackle. That’s as a result of hash-based addressing ends in URLs that aren’t straightforward to spell out or kind.
As an illustration, you will discover the Wikipedia emblem on IPFS through the use of the next tackle in an appropriate browser:
ipfs://QmRW3V9znzFW9M5FYbitSEvd5dQrPWGvPvgQD6LM22Tv8D/. That lengthy string could be regarded as a digital fingerprint for the file holding that emblem.
There are different content-addressing schemes that use human-readable naming, or hierarchical, URL-style naming, however every comes with its personal set of trade-offs. Discovering sensible methods to make use of human-readable names with IPFS would go a good distance towards bettering user-friendliness. It’s a purpose, however we’re not there but.
Protocol Labs, has been tackling these and different technical, usability, and societal points for a lot of the final decade. Over this time, we’ve been seeing quickly rising adoption of IPFS, with its community measurement doubling 12 months over 12 months. Scaling up at such speeds brings many challenges. However that’s par for the course when your intent is altering the Web as we all know it.
Widespread adoption of content material addressing and IPFS ought to assist the entire Web ecosystem. By empowering customers to request precise content material and confirm that they obtained it unaltered, IPFS will enhance belief and safety. Decreasing the duplication of knowledge shifting by way of the community and procuring it from close by sources will let ISPs present quicker service at decrease price. Enabling the community to proceed offering service even when it turns into partitioned will make our infrastructure extra resilient to pure disasters and different large-scale disruptions.
However is there a darkish facet to decentralization? We regularly hear issues about how peer-to-peer networks could also be utilized by dangerous actors to help criminality. These issues are essential however generally overstated.
One space the place IPFS improves on HTTP is in permitting complete auditing of saved knowledge. For instance, because of its content-addressing performance and, specifically, to the usage of distinctive and everlasting content material identifiers, IPFS makes it simpler to find out whether or not sure content material is current on the community, and which nodes are storing it. Furthermore, IPFS makes it trivial for customers to determine what content material they distribute and what content material they cease distributing (by merely deleting it from their machines).
On the identical time, IPFS supplies no mechanisms to permit for censorship, on condition that it operates as a distributed P2P file system with no central authority. So there is no such thing as a actor with the technical means to ban the storage and propagation of a file or to delete a file from different friends’ storage. Consequently, censorship of undesirable content material can’t be technically enforced, which represents a safeguard for customers whose freedom of speech is underneath risk. Lawful requests to take down content material are nonetheless doable, however they should be addressed to the customers truly storing it, avoiding commonplace abuses (like illegitimate
DMCA takedown requests) in opposition to which massive platforms have difficulties defending.
In the end, IPFS is an open community, ruled by group guidelines, and open to everybody. And you may change into part of it at this time! The
Courageous browser ships with built-in IPFS help, as does Opera for Android. There are browser extensions accessible for Chrome and Firefox, and IPFS Desktop makes it straightforward to run a neighborhood node. A number of organizations present IPFS-based internet hosting providers, whereas others function public gateways that help you fetch knowledge from IPFS by way of the browser with none particular software program.
These gateways act as entries to the P2P community and are essential to bootstrap adoption. By some easy DNS magic, a website could be configured so {that a} person’s entry request will consequence within the corresponding content material being retrieved and served by a gateway, in a manner that’s fully clear to the person.
Up to now, IPFS has been used to construct diverse purposes, together with techniques for
e-commerce, safe distribution of scientific knowledge units, mirroring Wikipedia, creating new social networks, sharing most cancers knowledge, blockchain creation, safe and encrypted personal-file storage and sharing, developerinstruments, and knowledge analytics.
You might have used this community already: In the event you’ve ever visited the Protocol Labs web site (
Protocol.ai), you’ve retrieved pages of an internet site from IPFS with out even realizing it!
From Your Web site Articles
Associated Articles Across the Net
[ad_2]
