[ad_1]
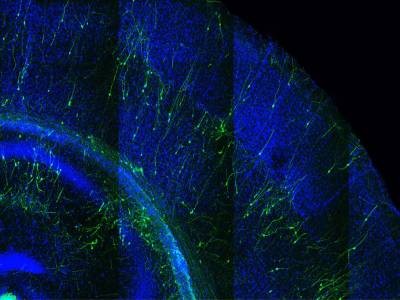
Researchers have transplanted a human mind organoid (shiny inexperienced) into the mind of a new child rat pup, creating hybrid brains during which the neurons interface.Credit score: Stanford College
Miniature human brain-like buildings transplanted into rats can ship indicators and reply to environmental cues picked up by the rats’ whiskers, based on a examine1. This demonstration that neurons grown from human stem cells can interface with nerve cells in reside rodents might result in a solution to take a look at therapies for human mind problems.
Hybrid brains: the ethics of transplanting human neurons into animals
Scientists want to use mind organoids — tiny brain-like buildings grown from human stem cells — to check neurodegenerative and neuropsychiatric problems that people develop. However the organoids mimic human brains solely up to now. They don’t develop blood vessels and so can’t obtain vitamins, which means that they don’t thrive for lengthy. They usually don’t obtain the mandatory stimulation to develop absolutely: in a human toddler’s mind, neurons’ development and growth of connections with different neurons is predicated partially on enter from the senses.
To present mind organoids this stimulation and help, neuroscientist Sergiu Pasca at Stanford College in California and his colleagues grew the buildings from human stem cells after which injected them into the brains of new child rat pups, with the expectation that the human cells would develop together with the rats’ personal cells. The crew positioned the organoids in a mind area known as the somatosensory cerebral cortex, which receives indicators from the rats’ whiskers and different sensory organs after which passes them alongside to different mind areas that interpret the indicators.
Can lab-grown brains grow to be aware?
Human mind cells mature rather more slowly than rat cells, so the researchers needed to anticipate greater than six months for the organoids to grow to be absolutely built-in into the rat brains. However once they examined the animals’ brains on the finish of that point, they noticed that the combination had been so profitable that it was virtually like including “one other transistor to a circuit”, Pasca stated at a ten October press convention.
Paola Arlotta, a molecular biologist at Harvard College in Cambridge, Massachusetts, is worked up concerning the outcomes. “It’s an necessary step in permitting organoids to inform us extra complicated properties of the mind,” she says, though she thinks that the transplantation process might be nonetheless too costly and sophisticated to grow to be a normal analysis instrument. The subsequent step, Arlotta provides, might be to work out how particular person human neurons — not simply absolutely developed organoids — are built-in into the rat mind.
Behaviour set off
Of their report, revealed in Nature on 12 October1, the researchers describe how they genetically engineered the neurons within the organoids to fireplace when stimulated with gentle from a fibre-optic cable embedded within the rats’ brains. The crew skilled the rats to lick a spout to obtain water whereas the sunshine was switched on. Afterwards, when the researchers shone the sunshine on the hybrid brains, the rats had been prompted to lick the spout, which means that the human cells had grow to be built-in effectively sufficient to assist drive the animals’ behaviour. Moreover, when the researchers tweaked the rats’ whiskers, they discovered that the human cells within the sensory cortex fired in response, suggesting that the cells had been in a position to decide up sensory data.
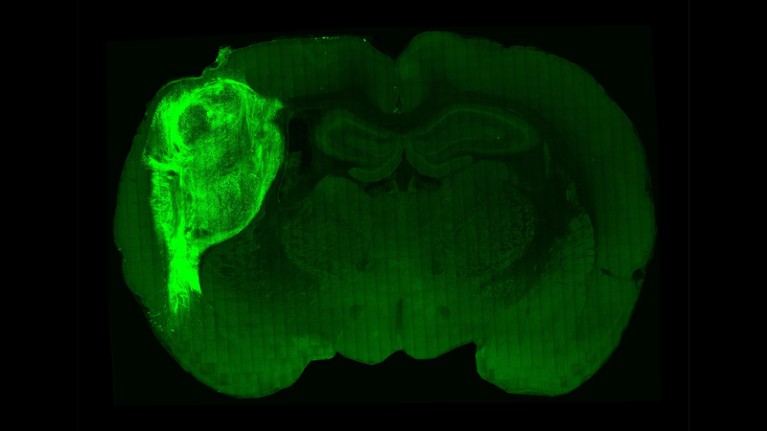
Human neurons created from stem cells and transplanted right into a rat mind (proper) develop extra absolutely than these cultivated in a dish (left).Credit score: Stanford College
To show the promise of their work for learning mind problems, Pasca and his colleagues additionally created mind organoids from the stem cells of three individuals with a genetic situation known as Timothy syndrome, which may trigger signs much like some seen in autism. The tiny buildings regarded the identical as every other mind organoids grown in a dish, however when the researchers transplanted them into rats, they didn’t develop as massive as others and their neurons didn’t fireplace in the identical approach.
Rusty Gage, a neuroscientist on the Salk Institute for Organic Research in La Jolla, California, is glad to see these outcomes. In 2018, he and a crew of researchers discovered that transplanted human mind organoids might be built-in into the brains of grownup mice2. Mice don’t reside so long as rats, so Pasca and his colleagues hoped that as a result of new child rat pups’ brains are extra plastic than these of grownup animals, that they might be higher in a position to obtain the brand new cells.
“We’ve obtained challenges on the market for us,” Gage says. “However I do imagine the transplantation process might be a precious instrument.”
First monkey–human embryos reignite debate over hybrid animals
A number of the challenges are moral. Persons are involved that creating rodent–human hybrids might hurt the animals, or create animals with human-like brains. Final yr, a panel organized by the US Nationwide Academies of Sciences, Engineering, and Drugs launched a report concluding that human mind organoids are nonetheless too primitive to grow to be aware, attain human-like intelligence or purchase different skills that may require authorized regulation. Pasca says that his crew’s organoid transplants didn’t trigger issues similar to seizures or reminiscence deficits within the rats, and didn’t appear to alter the animals’ behaviour considerably.
However Arlotta, a member of the Nationwide Academies panel, says that issues might come up as science advances. “We are able to’t simply talk about it as soon as and let or not it’s,” she says. She provides that issues about human organoids must be weighed towards the wants of individuals with neurological and psychiatric problems. Mind organoids and human–animal hybrid brains might reveal the mechanisms underlying these sicknesses, and permit researchers to check therapies for circumstances similar to schizophrenia and bipolar dysfunction. “I believe we’ve a duty as a society to do every part we will,” Arlotta says.
[ad_2]