[ad_1]
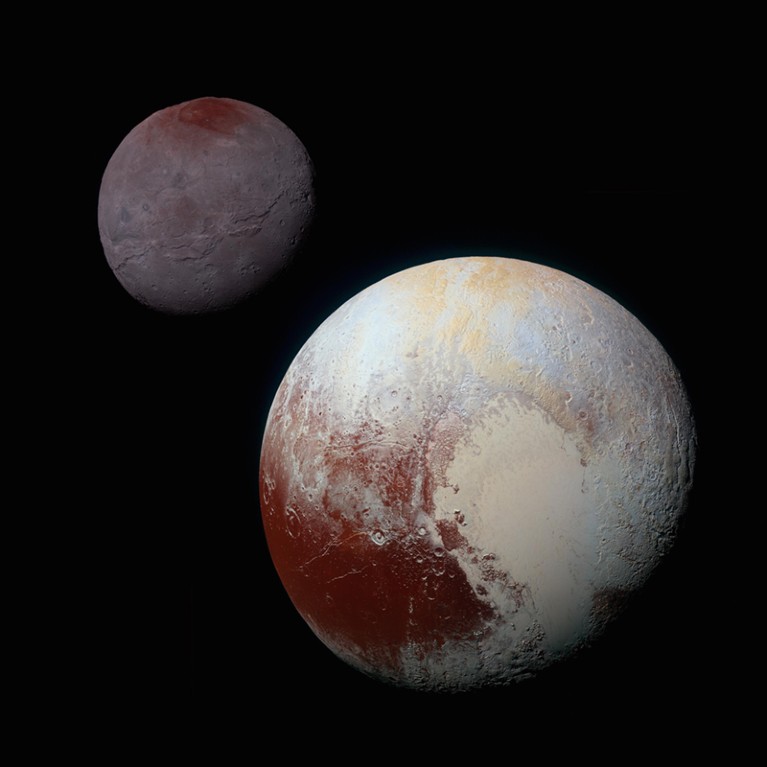

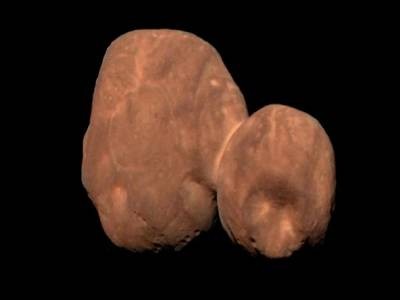
NASA’s New Horizons spacecraft snapped this picture of Pluto (decrease proper) and its moon Charon (higher left) because it handed by in 2015.Credit score: NASA/Johns Hopkins College Utilized Physics Laboratory/Southwest Analysis Institute
Within the distant reaches of the Photo voltaic System, greater than 8 billion kilometres from Earth, NASA’s New Horizons spacecraft is on the centre of a dispute over its future.
Pluto’s geology is in contrast to every other
The craft, which snapped gorgeous photographs throughout humanity’s first go to to Pluto in 2015, is inside a couple of years of exiting the Kuiper belt, the realm of frozen objects that orbit the Solar past Neptune. Along with Pluto, it has flown previous one other Kuiper belt object referred to as Arrokoth, however has not discovered a 3rd object to go to earlier than it leaves. So NASA now plans to repurpose the spacecraft primarily as a heliophysics mission, to review house climate and different phenomena that it will possibly measure from its distinctive location within the Photo voltaic System.
However some are sad with the choice, and fear that planetary research are being truncated too quickly. “Scientifically, I simply don’t really feel that we’re at diminishing returns but,” says Kelsi Singer, the mission’s mission scientist on the Southwest Analysis Institute in Boulder, Colorado.
Shifting New Horizons from being a planetary explorer to an interstellar emissary echoes what the company did with the dual Voyager spacecraft after they visited the outer planets within the Nineteen Eighties. “Now we have this completely working spacecraft that’s in a singular space,” says Nicola Fox, head of NASA’s science mission directorate in Washington DC. The company desires to get the “greatest use” out of it, she says, in addition to “open it as much as as many scientists from as many disciplines as have an interest”.
A mission takeover?
Nobody disputes that New Horizons has made gorgeous discoveries within the Kuiper belt, which accommodates particles left over from the Photo voltaic System’s early historical past. The spacecraft has uncovered secrets and techniques of Pluto’s icy floor and revealed extra about how the constructing blocks of planets might need come collectively. Its 2019 fly-by of Arrokoth, a 35-kilometre-long Kuiper belt object made from two chunks of stuck-together house rock, “taught us a lot about basic properties of planetary formation — utterly transformational”, says Michele Bannister, a planetary scientist on the College of Canterbury in Christchurch, New Zealand.
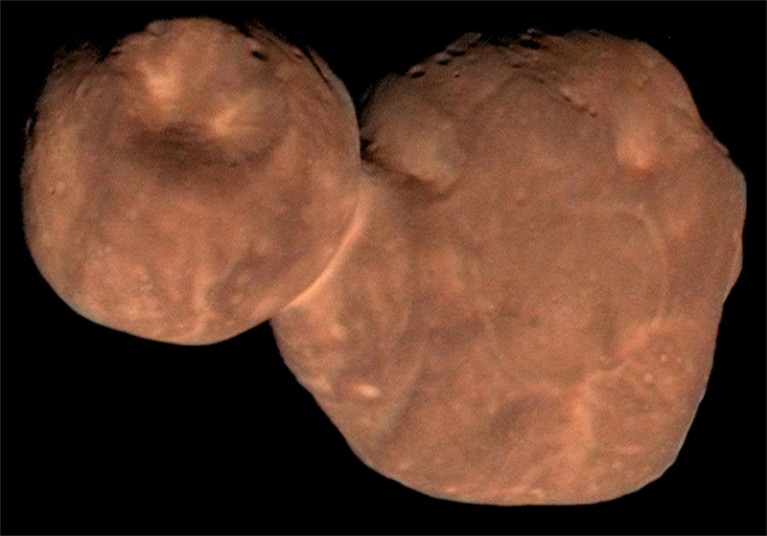
New Horizons visited the Kuiper belt object Arrokoth in 2019.Credit score: NASA/Johns Hopkins College Utilized Physics Laboratory/Southwest Analysis Institute/Roman Tkachenko
With out one other Kuiper belt object to fly by, the planetary science for New Horizons turns into tougher to justify, some say. Tensions arose final 12 months after NASA’s planetary science division carried out a ‘senior overview’ of its operational missions, because it does each few years. A panel of scientists evaluated eight missions, together with New Horizons, for his or her latest scientific efficiency and future promise.
That overview rated New Horizons’ present science as “glorious/excellent” if planetary science, astrophysics and heliophysics have been all included. The score slid to “excellent/good” for planetary science alone, partially as a result of the science crew’s proposed research of Kuiper belt objects have been “unlikely to dramatically enhance the state of data”, the overview stated. (The mission’s science crew disputes that conclusion.)
NASA used the overview in its determination to shift the spacecraft to being managed as a heliophysics mission, says Lori Glaze, head of the company’s planetary science division. “As a result of that’s the place the power lies — within the science that may be carried out from right here ahead,” she says.
Photo voltaic System’s distant snowman comes into sharp focus
NASA will fund the mission from its planetary science funds till 30 September 2024. After that, administration may very well be taken over by the a lot smaller heliophysics division, doubtlessly involving a brand new group of scientists. In March, NASA requested US researchers for concepts on what science New Horizons might do throughout all disciplines, “to gauge the extent of curiosity of the broader science group in pursuing the subsequent section of science management for the mission, and to estimate applicable annual prices”.
To the mission’s present science crew, this quantities to a takeover. “There’s going to be a boarding social gathering on the primary of October subsequent 12 months,” says Alan Stern, the mission’s principal investigator, who can also be on the Southwest Analysis Institute. Fox responds that the New Horizons crew was invited to submit a proposal to guide the spacecraft’s science within the heliophysics division beginning in October 2024, and that the researchers declined.
Full substitute of a mission’s science crew is comparatively uncommon, says Amanda Hendrix, a researcher on the Planetary Science Institute in Boulder, Colorado. “That is sort of new territory that we’re moving into.”
In a ‘distinctive place’
Now the query is what science can nonetheless be completed with New Horizons, and the way. Though its plutonium energy supply is waning with time, it has sufficient to final most likely one other quarter of a century.
The craft is at present within the outer a part of the Kuiper belt (see ‘On the market’), about which little is thought as a result of it will possibly’t be noticed effectively from Earth. “New Horizons is in a really distinctive place, and there’s principally no different method to get this info,” Singer says.
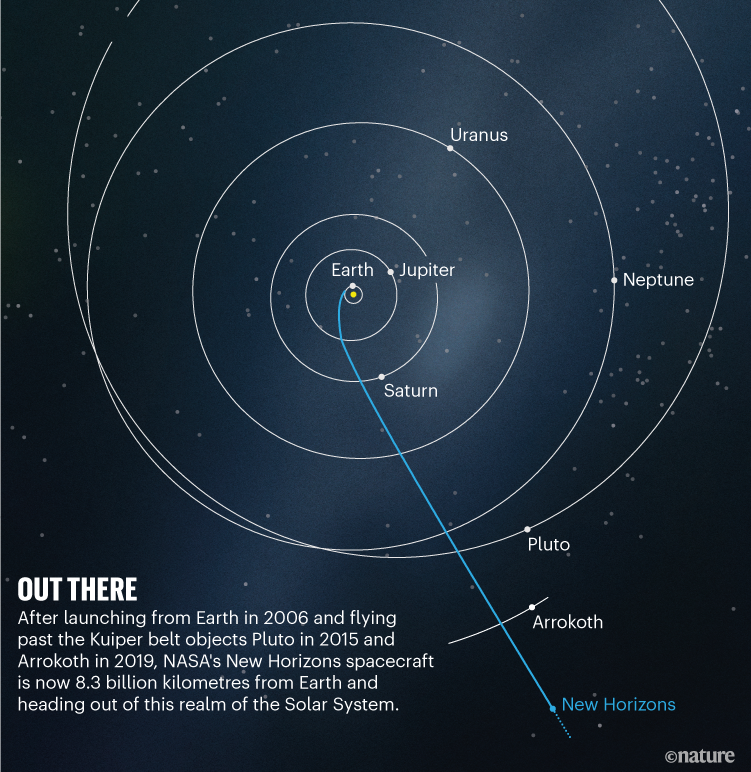
Supply: NASA/Johns Hopkins College Utilized Physics Laboratory/Southwest Analysis Institute
Amongst different research, New Horizons has been taking repeated photos of distant Kuiper belt objects, build up info on their shapes and floor properties. The spacecraft additionally analyses mud within the Kuiper belt — knowledge that may make clear how usually house rocks smash into one another.
Lately, the spacecraft has begun to broaden its focus. In astrophysics, New Horizons’ location permits it to review a number of varieties of background gentle that permeate the Photo voltaic System. And in heliophysics, ongoing and future research are exploring the floods of charged particles emanating from the Solar. “It’s very useful along side the 2 Voyagers,” says Stamatios Krimigis, an area physicist and the one scientist who has been concerned with missions to the entire Photo voltaic System’s planets and Pluto.
New Horizons, which price US$780 million to construct, launch and fly previous Pluto, at present prices NASA round $10 million yearly. Each Fox and Glaze advised Nature that the choice to shift the mission away from planetary science was not pushed by budgetary points, akin to those who have delayed a Venus mission and raised issues over the price of Mars pattern return.
Each additionally stated that if a Kuiper belt object have been discovered that New Horizons might attain, NASA could be open to discussing that, even when the mission had already been shifted to heliophysics. Stern and his crew proceed to search for a fly-by goal within the time they’ve left.
[ad_2]