[ad_1]
This week, the leaders of the Group of Seven (G7) economies — Canada, France, Germany, Italy, Japan, the UK and the US, plus the European Union — will assemble in Hiroshima, Japan, for his or her forty ninth summit. Local weather motion will, rightly, be excessive on the agenda. With local weather impacts mounting and the transition to low-carbon power at a crossroads, the group should guarantee that the motion it takes is swift and decisive, and works each in its member international locations’ greatest pursuits and in these of the broader world.
International management from the G7 is essential for slicing greenhouse-gas emissions shortly to maintain planetary warming throughout the 1.5–2 °C threshold of the Paris local weather settlement1. G7 actions matter as a result of the group accounts for greater than half of world gross home product (GDP), 28% of carbon dioxide emissions from fossil fuels and 13% of the world’s inhabitants, in addition to a big share of historic emissions2. It additionally has the monetary means to help different international locations in creating more-ambitious decarbonization objectives.
Local weather commitments already made by the G7 must be expanded and market distortions hindering the inexperienced transition must be eliminated. In 2020 and 2021, the group spent greater than US$725 billion on inexperienced measures, similar to clear power, power effectivity, electrical autos and green-innovation analysis, as a part of packages for financial restoration from the worldwide slowdown that accompanied the COVID-19 pandemic3.
However on the identical time, market distortions favouring fossil fuels stay4. Throughout the G7 international locations, subsidies — similar to incentives for elevated manufacturing, write-offs and tax deductions and decreasing costs paid by customers — for oil, coal and fuel quantity to $63 billion per 12 months, or $62 per particular person, on common5. Artificially depressed costs deter quick progress of low-carbon power and have helped to spur a post-pandemic surge in fossil-fuel consumption and greenhouse-gas emissions6. However the true value is way larger. Including within the environmental and well being prices of fossil-fuel use, together with local weather impacts, air pollution, visitors congestion and street accidents, in addition to forgone tax revenues, underpricing fossil fuels is costing the G7 nations virtually $1.2 trillion every year — 2.8% of the G7’s GDP and $1,186 per particular person5. For the remainder of the world, the price is $4.7 trillion (see ‘The true worth of fossil fuels’).
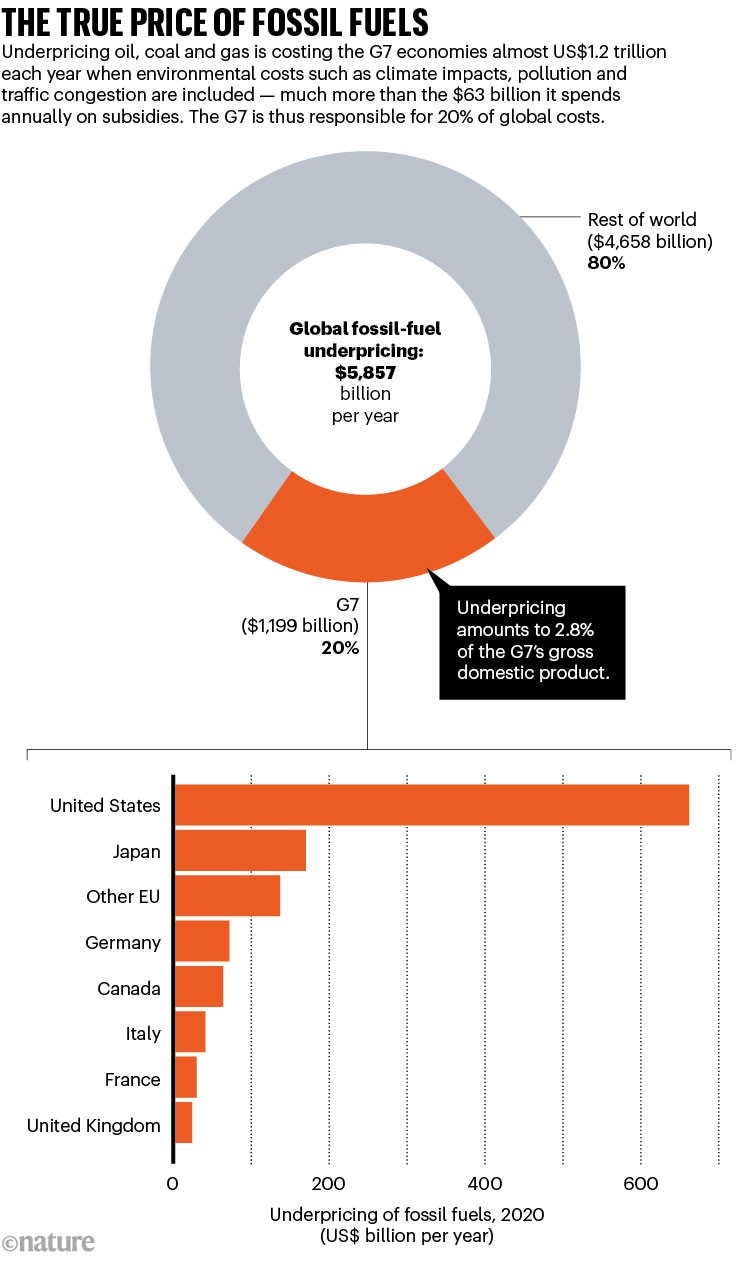
Supply: IMF (go.nature.com/3KKHML)
Authorities funding in inexperienced tech analysis and improvement (R&D) is flagging in G7 nations simply when it’s wanted most. Though renewables took a rising share of power R&D public spending from the Nineteen Nineties to the 2000s, reaching a peak of 15–30% of the overall in all 7 economies in 2010, since 2015 that share has fallen to round 10–20% of the overall7. Authorities-funded R&D associated to the atmosphere is caught at 1.5–3% for six of the G7 economies and at simply 0.3% in the US in 20217. Lapsing innovation within the G7 might need slowed environmental-technology improvement globally (see ‘A fall in inexperienced innovation’). Over 2016–19, the G7 accounted for 70% of world inexperienced innovation, with the US and Japan every producing 21% and Germany 11%7.
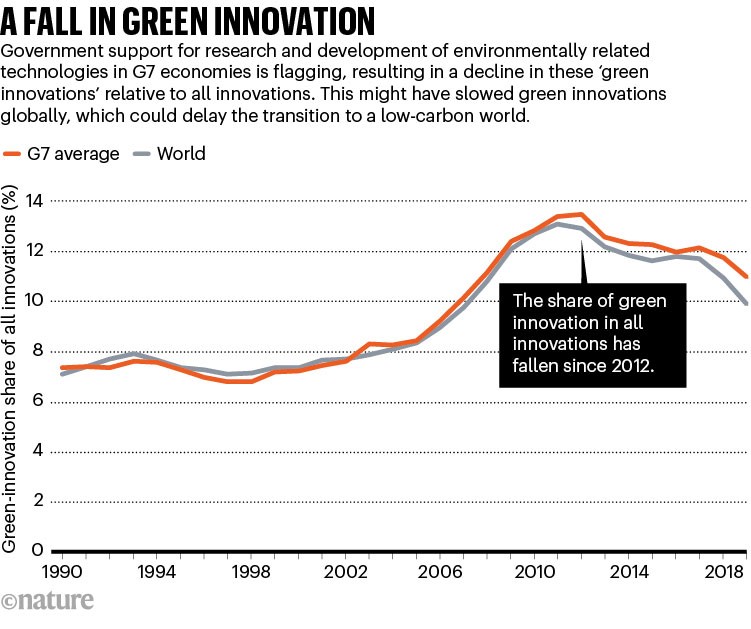
Supply: OECD
The G7 has taken some constructive steps. On the 2022 summit in Germany, the group agreed to kind a ‘Local weather Membership’ to spur the introduction of more-ambitious local weather insurance policies; its formal launch is predicted later this 12 months. Finally, the group intends different international locations to hitch, and the G7 and different members are contemplating whether or not or to not impose levies on imported items, on the idea of their embodied carbon emissions. The purpose could be to decarbonize emission-intensive and trade-exposed industries, similar to cement, chemical substances, iron and metal, whereas defending these industries from competitors in international locations that haven’t adopted comparable initiatives.
However the G7 can and may do rather more, inside its personal borders and within the wider world. Final month, I outlined a three-tiered low-carbon technique in a coverage paper for the Hiroshima summit (see go.nature.com/3lduqd2). The gist of it, outlined right here, is that the G7 ought to undertake three core units of insurance policies: to beat market distortions favouring fossil fuels; to foster a more-inclusive model of the Local weather Membership; and to help emerging-market and creating economies to realize local weather, poverty-alleviation and improvement objectives.
Take away market distortions favouring fossil fuels
All G7 members ought to begin by implementing three inexperienced insurance policies to scale back greenhouse-gas emissions from fossil-fuel use. First, they need to section out all subsidies for consuming and producing fossil fuels over the following 5 years. This may lower your expenses and make economies extra sustainable, power unbiased and safe.
Second, they need to section in more-comprehensive carbon-pricing mechanisms. These contain both carbon taxes or emission-trading schemes, each of which successfully put a cost on every tonne of carbon produced. A tax imposes this cost immediately, whereas emission buying and selling locations an total cap on air pollution and permits polluters to commerce their allotted emission permits. The ensuing traded worth for permits turns into the cost for emitting carbon. Though a number of G7 economies have launched carbon taxes and emission buying and selling to restrict greenhouse-gas emissions, usually carbon costs stay too low to incentivize modifications in behaviour, and the scope of those mechanisms is simply too slender.
Why we want a brand new economics of water as a standard good
To be on observe for internet zero emissions by 2050, high-income and huge emitters similar to these within the G7 ought to attain a carbon worth of no less than $75 per tonne of carbon dioxide emitted and prolong the pricing to cowl extra sectors8. No G7 member does each (see Supplementary Desk 1). For instance, the European Union Emissions Buying and selling System has reached larger worth ranges however covers solely energy, manufacturing and aviation. Japan’s carbon worth is extraordinarily low — $2 per tonne of carbon dioxide equal (tCO2e) — however does cowl all sectors (with some exemptions)9. The USA at the moment has no nationwide carbon pricing scheme but it surely might encourage states and cities to tax and commerce carbon extra extensively, as California, Oregon, Washington and the Regional Greenhouse Fuel Initiative of 12 jap states at the moment do.
Third, G7 international locations ought to direct the revenues raised in direction of inexperienced priorities, together with investments in clean-energy R&D and transport infrastructure. Governments ought to offset hostile results on revenue, employment and inequality by elevating the minimal wage, offering funds or retraining for displaced employees, and focusing on revenue dividends and tax rebates to weak households. Insurance policies alongside these strains in Italy, France, Germany, Spain, Norway and Estonia cushioned the impacts of the energy-price surge following the Russian invasion of Ukraine, for instance10. Absolutely compensating the underside 20% of all European households for the 2021–22 energy-price surge would have value every nation, on common, 0.4% of GDP10.
Make the Local weather Membership globally inclusive
The G7’s Local weather Membership initiative is a step in the fitting route, however from a world perspective, its success will hinge on how successfully different nations might be introduced in. Within the second key set of actions I suggest, the G7 ought to prolong its Local weather Membership with a more-inclusive framework. To be efficient in encouraging members to scale back emissions, a local weather membership should agree on a minimal carbon worth for members and impose penalties on international locations that don’t take part11. However the G7, and the world, will reap extra advantages by additionally permitting different international locations to hitch. If different massive emitters stay exterior, industries primarily based within the G7 would possibly change into much less aggressive and a few will swap manufacturing to nations with fewer restrictions, decreasing emissions financial savings8.

A wind turbine spins in entrance of the cooling towers on the Jänschwalde coal-fired energy station in Germany.Credit score: Sean Gallup/Getty
Committing to take away market distortions favouring fossil fuels must be the primary precondition for any nation becoming a member of the Local weather Membership. As an incentive, minimal carbon costs must be set decrease for emerging-market and creating economies that change into members. For instance, costs might be set at $75 per tCO2e emitted for high-income international locations, $50 per tonne for middle-income international locations and $25 per tonne for low-income international locations8,12. Such a differentiated worth ground is progressive as a result of it would induce proportionally extra carbon mitigation by high-income international locations.
Contributors within the membership might obtain the value ground by means of both pricing carbon or equal insurance policies, similar to rules that restrict emissions and develop the sectors lined and by commitments from states, provinces, cities and companies. Initially, the carbon worth ground might be only for energy technology and carbon-intensive industries similar to cement, iron, metal and chemical substances. Later, it might be prolonged to different sectors and sources from business, companies, transport and agriculture. Particular person international locations might set larger carbon costs to realize more-ambitious mitigation pledges and targets.
Power disaster: 5 questions that have to be answered in 2023
The G7 Local weather Membership may also have to impose a carbon import levy — a cost on the carbon embodied in imports from areas which have but to undertake the membership’s minimal carbon pricing. Subsequently, a ‘border carbon adjustment’ is important to guard the collective insurance policies and competitiveness of carbon-intensive industries of membership members13. Mixed with a differentiated carbon worth ground, the import levy would enable economies within the membership to implement formidable mitigation insurance policies for his or her carbon-intensive industries and encourage others to hitch the membership8. Rising-market and creating economies are more likely to reply by imposing a carbon worth on their very own industrial sectors and finally take part within the membership8.
Help creating economies to decarbonize
The G7 ought to go additional in aiding emerging-market and creating economies with adopting the insurance policies and investments wanted to take part within the Local weather Membership. That entails scaling up and broadening G7 initiatives such because the Simply Power Transition Partnerships (JETPs) and the Partnership for International Infrastructure and Funding (PGII).
The JETPs are a financing cooperation mechanism created by the G7 wherein donors assist to fund particular investments in rising economies, with the purpose of decreasing fossil-fuel dependency and over-reliance on coal, to speed up a clean-energy transition. The primary partnership was established between G7 members and South Africa at COP26 in Glasgow, UK, in 2021. Two extra partnerships had been launched with Indonesia and Vietnam final 12 months, and two extra are deliberate with Senegal and India. Nonetheless, these plans are nonetheless imprecise. Some G7 companions — the EU, France, Germany, the UK and the US — have pledged $8.5 billion in technical and monetary help to South Africa for clear electrical energy, electrical autos and inexperienced hydrogen tasks, however with few specifics14.
Degrowth can work — right here’s how science may also help
The PGII, introduced on the 2022 G7 summit in Germany, seeks to mobilize $600 billion in international infrastructure investments from private and non-private sources by 2027; the US has pledged $200 billion already, and additional particulars on implementing the fund are more likely to emerge on the Hiroshima summit. It ought to prioritize investments that complement and help these made by means of the JETPs. This would possibly embody enhancing transmission grids to help clear power, more-sustainable city improvement, decarbonizing industries and creating charging networks for electrical autos.
In return, accomplice nations ought to undertake carbon pricing and different insurance policies mandatory to hitch the Local weather Membership. The G7 ought to help them with finance and the design and implementation of local weather insurance policies. This could be coordinated by means of the World Financial institution’s Partnership for Market Implementation Facility, which goals to place carbon-pricing insurance policies and programmes in place in no less than 30 rising and creating economies; G7 help would allow extra international locations to be introduced in.
Such insurance policies ought to ideally be designed to realize poverty alleviation, improvement and climate-mitigation objectives concurrently, particularly in rural areas. Two promising insurance policies are swapping out fossil-fuel subsidies to offer enlargement of renewable-energy companies in underserved rural areas; and utilizing revenues from carbon pricing to fund nature-based options, similar to planting forests, that create jobs and livelihoods in poor areas.
By all these means, creating the circumstances for an inclusive Local weather Membership will allow the G7 to speed up a low-carbon transition of their economies and encourage extra nations to do the identical.
[ad_2]



