[ad_1]
Final yr, round two-thirds of Pakistan was affected by widespread flash flooding, with greater than 1,500 folks killed and round 33 million made homeless. Nearly 2,000 folks died in flash floods throughout Africa, and elements of the United Arab Emirates, Iran, Saudi Arabia, Qatar, Oman and Yemen have been inundated with water.
Flash floods are a rising risk in a number of the world’s driest areas. Deluges can set off sudden and speedy torrents of run-off that movement down dry river beds and rocky channels.
As a result of parched soils repel water relatively than permitting it to soak in, flash floods could be extra devastating in drylands than in wetter areas. Surges may end up from comparatively small quantities of rain, as little as 10 millimetres in a single hour. By comparability, floods in wetter areas sometimes observe extra extended bouts of rainfall.
Speedy run-off additionally erodes soils, including sediment and particles to the water. The hazards are best in mountainous areas, the place water can gush abruptly by gullies and down slopes. For instance, a flash flood final yr in Datong city in Qinghai province, China, washed away greater than 1,500 properties in lower than one hour.
But residents of drylands are underprepared for flash floods, in contrast with folks within the tropics. In dry areas, the place drought is a giant concern, settlements are typically close to rivers or on floodplains. Dams and levees are low priorities.
Dryland residents are paying a excessive value. Our evaluation utilizing the Emergency Occasions Database (EM-DAT; www.emdat.be) reveals that, since 2000, such areas skilled lower than half (47%) of lethal flash floods globally, but noticed virtually three-quarters (74%) of associated deaths (see ‘World flash-flood disasters’). Nearly all of these floods (87%) and related deaths (97%) occurred in low- and middle-income international locations.
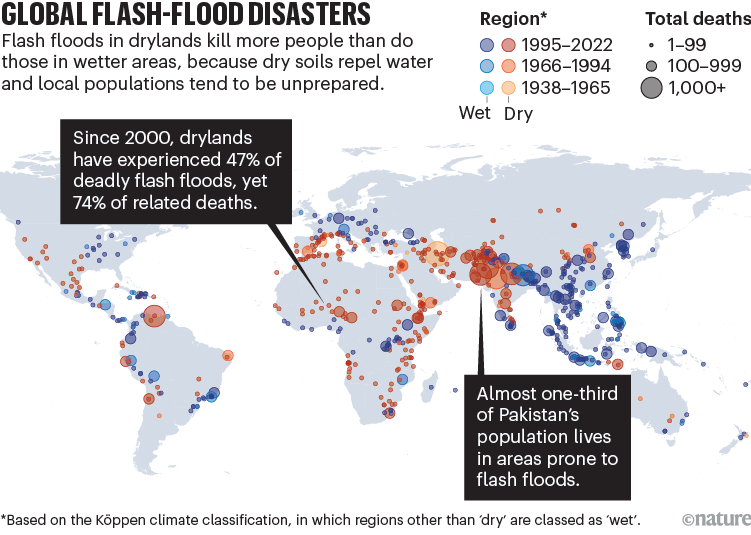
Supply: EM-DAT, CRED/UC Louvain (www.emdat.be); Evaluation by J. Yin et al.
A slew of different components will put many extra folks in danger from flash floods in future (see ‘Drylands: flash-flood dangers’). Local weather change is making such occasions extra intense and frequent1–3. In elements of Pakistan, for instance, the 5-day most stage of rainfall is 75% better immediately than it was earlier than 1900 (see go.nature.com/41awzzj). Our evaluation reveals that globally, the speed of dryland flash flooding was 20 instances increased between 2000 and 2022 than it was between 1900 and 1999 (numbering 278 and 64 floods, respectively).
Extra persons are dwelling in drylands — from 40% of the worldwide inhabitants in 2000 to 44% in 2020, by our calculation. Such areas will host 51% of the world’s inhabitants development by 2025, with half of these folks dwelling in low-income international locations, and just one% in developed ones4. Cities are increasing quickly in areas such because the Center East, India and China5. And the proportion of the world’s land space classed as arid or semi-arid is projected to extend because the world warms — from 41% in 2000 to 48% by 20254.
Pakistan is without doubt one of the most uncovered nations. Nearly one-third of the nation’s inhabitants (72 million of 230 million folks) lives in high-risk flash-flood zones. As ever, susceptible teams corresponding to older folks, girls and youngsters expertise the worst results.
Researchers, practitioners and policymakers must mannequin, assess and mitigate the danger of flash flooding in drylands in a altering atmosphere. Right here, we set out six analysis priorities for doing so.
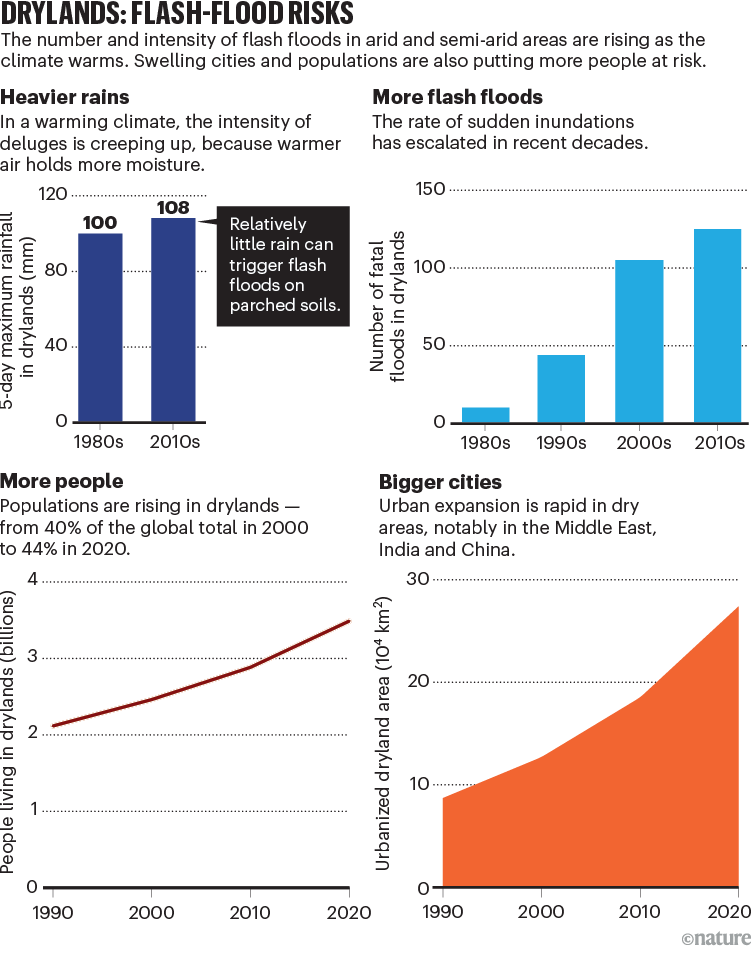
Supply: EM-DAT, CRED/UC Louvain (www.emdat.be); Evaluation by J. Yin et al.
Collect knowledge and map the dangers
Assessing the probability and penalties of flash floods requires numerous knowledge. These embody: meteorological and hydrological measurements; topographic knowledge and digital elevation fashions; data of property and former losses; and census knowledge. Nevertheless, most dryland areas lack a lot of this data, as a result of nationwide governments usually don’t acknowledge its worth and plenty of lack the sources to assemble it.
Researchers, worldwide organizations and non-governmental organizations want to assist such international locations to replace their flood-risk data. Initiatives embody the World Flood Partnership run by the European Union (https://gfp.jrc.ec.europa.eu), which is growing flood statement and modelling infrastructure in low- to middle-income international locations corresponding to Myanmar. Governments ought to map flash-flood dangers and distribute them on-line (as the UK does; see go.nature.com/3xt9hfz) to pinpoint places which are liable to flooding, limit building and goal flood-protection measures.
Flood danger must be fastidiously communicated, as a result of it may exacerbate inequalities. In drylands, low-income and minority populations are likely to reside in flood-prone areas corresponding to riversides6. If maps present these areas to be excessive danger, they might be disadvantaged of native infrastructure funding, growing their vulnerability. Socio-economic knowledge ought to subsequently even be conveyed to resolution makers alongside the maps.
Develop early-warning programs
Early-warning programs for flash floods are working in some rich international locations, together with america and in EU nations. For instance, the US system (FLASH) forecasts floor water flows at 10-minute intervals and with a spatial decision of 1 kilometre. These forecasts mix real-time observations from radar, satellites and sensors with hydrological fashions, and may present just a few hours’ discover of flash floods. If preparation and response plans are additionally in place, which may give sufficient time for governments to allocate rescue sources and for residents to guard properties and transfer to security factors. Nevertheless, few low- and middle-income nations have these programs, as a result of they lack the info and fashions to help them, in addition to political incentives and funding.
How local weather change and unplanned city sprawl carry extra landslides
To rectify this, the World Meteorological Group is operating a programme to offer climate forecasters and disaster-management companies with real-time data round flash-flood threats (see go.nature.com/3xsw4fg). To this point, 28 warning programs are up and operating, with one other 39 in improvement. Eight of the operational programs are in drylands, along with ten of these nonetheless in improvement. Extra dryland nations have to be engaged.
Forecasting of flash floods in drylands will want tailoring to native contexts, together with soil varieties, terrains and sediment hundreds. The place knowledge are scarce, uncertainties and limits have to be higher understood. Use of wi-fi sensors and various sources of native knowledge, corresponding to use of social media and crowdsourcing, have to be explored.
Enhance resilience to sudden floods
Dams, limitations and dikes will have to be put in in drylands to guard settlements. For instance, China has been constructing hundreds of kilometres of levees alongside the primary stream and tributaries of the Yellow River. That is costly, nonetheless, involving a whole lot of initiatives with prices starting from hundreds of thousands to billions of {dollars}.
Researchers want to look at the trade-offs. For instance, safety measures would possibly encourage extra improvement in flood-prone areas — as was the case in Columbia, South Carolina, which skilled intensive harm from a flash flood in 2015. And dams and levees constructed to carry again small floods might supply a false sense of safety from uncommon, excessive inundations7, together with one which flooded the Atacama area in South America in 2015. Failure of 1 safety aspect, corresponding to a reservoir, can ship flood waters cascading downstream, as was narrowly averted at California’s Oroville Dam in 2017. The environmental impacts have to be understood, corresponding to these ensuing from stopping the silt and sediment that fertilize the floodplain.
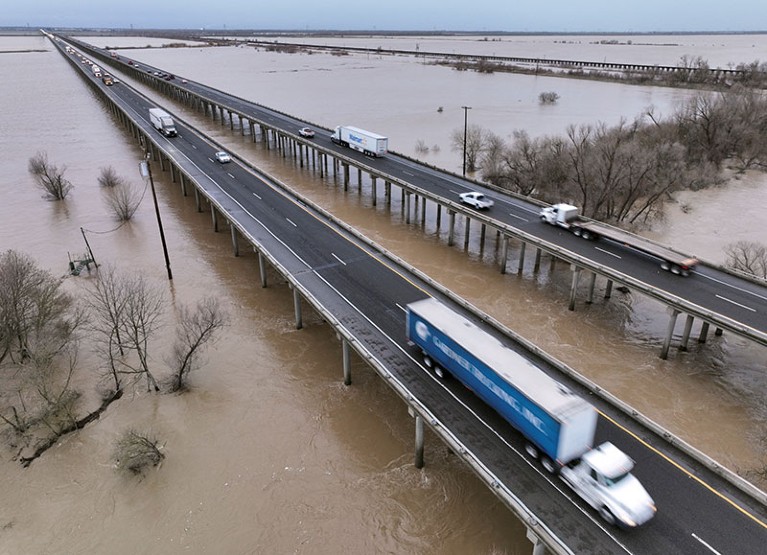

Autos cross a bridge over the Yolo Bypass in Sacramento, California, the place weirs divert flood waters away from homes onto floodplains.Credit score: Fred Greaves/Reuters
Nature-based options are cheaper. For instance, in Pakistan, the federal government of Khyber Pakhtunkhwa province has restored virtually 350,000 hectares of forests in its ‘Billion Tree Tsunami’ planting drive. Within the Yolo Bypass mission in Sacramento, California, levees are being changed with weirs to divert flood waters away from homes and onto pure floodplains. Massive residential areas ought to undertake ‘sponge metropolis’ methods that scale back run-off, corresponding to permeable pavements, inexperienced roofs, rainwater harvesting and swales (ditches). These are being put in in cities all through China, together with Xining in Qinghai province, the biggest metropolis on the Tibetan Plateau.
Researchers ought to goal to quantify how efficient pure options are at storing and conveying water, and the way resilient they’re to excessive floods. Native variations in soil and vegetation situations have to be thought-about. Extra must be recognized about how the programs degrade and the way to preserve them. Promising initiatives embody the World Financial institution’s World Program on Nature-Primarily based Options for Local weather Resilience and the Sindh Resilience Undertaking in Pakistan, in addition to government-led water and soil conservation initiatives within the Loess Plateau in north-central China.
Land-use laws have to be tightened, corresponding to by stopping casual improvement in floodplains. Flood-protection requirements for buildings have to be improved. For instance, the Worldwide Residential Code, used as the premise of many nationwide and native pointers, requires the bottom flooring of buildings to be 30 centimetres above the typical stage of a ‘as soon as a century’ flood. Such ranges now not replicate flood likelihood in a warming world.
Plan for long-term resettlement
In flood-prone areas, governments ought to develop plans for momentary and even everlasting resettlement. Elevated roads, evacuation routes and emergency shelters have to be designed, corresponding to these utilized in Indonesia for tsunamis and in america for hurricanes. In the long term, as climate-change impacts speed up, managed retreat may be required8. For instance, the Chinese language authorities has relocated greater than 600,000 folks from flash-flood zones within the arid mountains of southern Shaanxi province over the previous decade.
Managed resettlement is extra equitable and environment friendly than leaving folks to fend for themselves. Cross-disciplinary analysis in social science, geography, engineering and psychology is required to analyze the easiest way to handle retreat, by offering important providers and help whereas avoiding meals insecurity and misplaced livelihoods.
Present finance past catastrophe assist
Danger-transfer schemes — corresponding to flood insurance coverage, disaster bonds and solidarity funds — must be developed for drylands. For instance, China is growing a nationwide system of flood insurance coverage merchandise. These have been integrated into the nationwide emergency-management system and launched in dozens of pilot cities, together with Zhengzhou in Henan province. Such merchandise embody climate index insurance coverage, which provides compensation for lack of crops and livestock when rainfall exceeds a sure threshold. Disaster insurance coverage protects companies and residences in opposition to excessive occasions which are too costly for insurers to cowl, corresponding to tremendous typhoons or floods that happen solely as soon as in 1,000 years.
5 methods to make sure flood-risk analysis helps probably the most susceptible
Algeria has made disaster insurance coverage necessary. Each insurance coverage firm there should be a part of its nationwide Disaster Danger Insurance coverage Pool to cowl catastrophe losses in proportion to their market share. All properties have to be insured, with premiums set by the federal government.
Researchers want to check the impacts of such schemes, particularly on fairness. For instance, susceptible households dwelling in flood-prone zones won’t be capable to afford excessive premiums9. Round 50% of losses in rich international locations are lined by insurance coverage, however there’s lower than 10% protection in lots of poorer international locations. For instance, claims for Hurricane Sandy in america in 2012 lined 50% of the damages. Against this, after a record-breaking flash flood in China’s Henan province in July 2021, flood insurance coverage claims exceeded US$1.7 billion — solely 11% of the entire losses.
Partnerships between international locations — corresponding to China’s ‘Belt and Street’ mission and the ‘Construct Again Higher World’ initiative proposed by the G7 group of superior economies — must be sought to ascertain solidarity funds that may share the danger of huge disasters, because the EU has performed. The United Nations local weather ‘loss and harm’ fund, accepted final yr on the COP27 summit in Sharm El-Sheikh, Egypt, must be leveraged to finance long-term flood-risk discount in drylands, as soon as mechanisms are formulated.
Enhance public consciousness and responses
Individuals who reside in drylands have to be extra conscious of flash-flood dangers. Policymakers ought to supply steerage to assist residents to adapt their behaviours and take precautionary measures — corresponding to by putting in flood-protection buildings, figuring out evacuation routes and warning alerts, figuring out areas liable to flooding or landslides, and avoiding strolling or driving by flooded areas and standing water.
Researchers must discover how finest to speak the effectiveness of measures, and the way perceptions of danger affect responses to flash floods10. Social components have to be explored — corresponding to age, gender, training, revenue, possession, tradition, faith and political context. For instance, previous expertise is necessary for recognizing dangers and adapting behaviours. However, for uncommon occasions, recollections fade and solely catastrophes are remembered for a very long time.
Collective behaviours additionally have to be understood11. Social-media messages can present speedy details about places, impacts and responses to dryland floods, as revealed by knowledge mining and synthetic intelligence. Fashions can combine complicated human behaviour into quantitative danger assessments, to enhance administration methods. Provided that flood dangers are evolving, it is very important adapt insurance policies as data turns into out there. Interdisciplinary evaluation may even be wanted to judge the robustness of flood-resilience methods for a variety of dangers and future situations12.
Earlier than extra lives are misplaced, let’s supply dryland residents the means to guarantee their security.
[ad_2]


